Subwavelength terahertz imaging via virtual superlensing in the radiating near field
- PMID: 37852953
- PMCID: PMC10584837
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41949-5
Subwavelength terahertz imaging via virtual superlensing in the radiating near field
Abstract
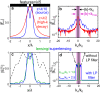
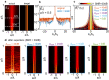
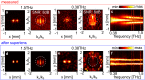
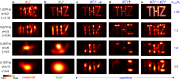
Imaging with resolutions much below the wavelength λ - now common in the visible spectrum - remains challenging at lower frequencies, where exponentially decaying evanescent waves are generally measured using a tip or antenna close to an object. Such approaches are often problematic because probes can perturb the near-field itself. Here we show that information encoded in evanescent waves can be probed further than previously thought, by reconstructing truthful images of the near-field through selective amplification of evanescent waves, akin to a virtual superlens that images the near field without perturbing it. We quantify trade-offs between noise and measurement distance, experimentally demonstrating reconstruction of complex images with subwavelength features down to a resolution of λ/7 and amplitude signal-to-noise ratios < 25dB between 0.18-1.5 THz. Our procedure can be implemented with any near-field probe, greatly relaxes experimental requirements for subwavelength imaging at sub-optical frequencies and opens the door to non-invasive near-field scanning.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Novotny, L., Hecht, B. Principles of Nano-Optics (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2012).
-
- Schermelleh L, et al. Super-resolution microscopy demystified. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019;21:72–84. - PubMed
-
- Adams W, Sadatgol M, Güney DÖ. Review of near-field optics and superlenses for sub-diffraction-limited nano-imaging. AIP Adv. 2016;6:100701.
-
- Keilmann F, Hillenbrand R. Near-field microscopy by elastic light scattering from a tip. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004;362:787–805. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, et al. Modern scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy for advanced material research. Adv. Mater. 2019;31:1804774. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

