Impact of experiencing multiple vulnerabilities on fetal growth and complications in women with hyperglycemia in pregnancy
- PMID: 37853313
- PMCID: PMC10585815
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-023-06048-9
Impact of experiencing multiple vulnerabilities on fetal growth and complications in women with hyperglycemia in pregnancy
Abstract
Background: In women with hyperglycemia in pregnancy living in France, psychosocial deprivation is associated with both earlier and greater exposure to the condition, as well as poorer maternofetal prognosis. We explored the impact of this and two other socioeconomic vulnerability indicators-food insecurity and poor language proficiency-on adherence to prenatal care and maternal and fetal outcomes.
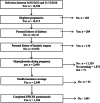
Methods: In a socially deprived suburb of Paris, we selected women who delivered between 01/01/2012 and 31/12/2018 and received care (nurse, dietician, diabetologist evaluation, advice, regular follow-up to adjust insulin doses if requested) for hyperglycemia in pregnancy. We analyzed the associations between individual psychosocial deprivation, food insecurity, French language proficiency (variables assessed by individual questionnaires) and fetal growth (main outcome), as well as other core maternal and fetal outcomes.
Results: Among the 1,168 women included (multiethnic cohort, 19.3% of whom were Europeans), 56%, 17.9%, and 27.5% had psychosocial deprivation, food insecurity, and poor French language proficiency, respectively. Forty-three percent were prescribed insulin therapy. Women with more than one vulnerability had more consultations for diabetes. The rates for small (SGA), appropriate (AGA), and large-for-gestational-age (LGA) infant were 11.4%, 76.5% and 12.2%, respectively. These rates were similar in women with and without psychosocial deprivation, and in those with and without food insecurity. Interestingly, women with poor French language proficiency had a higher odds ratio of delivering a small- or large-for-gestational age infant than those with good proficiency.
Conclusion: We found similar pregnancy outcomes for women with hyperglycemia in pregnancy living in France, irrespective of whether or not they had psychosocial deprivation or food insecurity. Optimized single-center care with specialized follow-up could contribute to reduce inequalities in maternal and fetal outcomes in women with hyperglycemia in pregnancy.
Keywords: Food insecurity; Hyperglycemia in pregnancy; Language proficiency; Large-for-gestational-age infant; Psychosocial deprivation; Small-for-gestational-age infant.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antagonistic effects of smoking and maternal glycemia on fetal growth: a retrospective study among 13,958 pregnant French women.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 14;16:1527358. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1527358. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40162319 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors of Small for Gestational Age and Large for Gestational Age at Buriram Hospital.J Med Assoc Thai. 2015 May;98 Suppl 4:S71-8. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015. PMID: 26201137
-
Cord blood metabolic markers are strong mediators of the effect of maternal adiposity on fetal growth in pregnancies across the glucose tolerance spectrum: the PANDORA study.Diabetologia. 2020 Mar;63(3):497-507. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05079-2. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 31915893
-
Large-for-Gestational-Age Neonates in Type 1 Diabetes and Pregnancy: Contribution of Factors Beyond Hyperglycemia.Diabetes Care. 2018 Aug;41(8):1821-1828. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0551. Diabetes Care. 2018. PMID: 30030258 Review.
-
The impact of occupational shift work and working hours during pregnancy on health outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Dec;221(6):563-576. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.06.051. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 31276631
Cited by
-
Associations between food insecurity in high-income countries and pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2024 Sep 10;21(9):e1004450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004450. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Med. 2024. PMID: 39255262 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycaemia in Pregnancy Is Less Frequent in Smokers: A French Observational Study of 15,801 Women.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 30;13(17):5149. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175149. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274361 Free PMC article.
-
Disparities in Diabetes in Pregnancy and the Role of Social Determinants of Health.Curr Diab Rep. 2025 May 14;25(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s11892-025-01587-1. Curr Diab Rep. 2025. PMID: 40366501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between food insecurity and the risk of pregnancy-induced hypertension: a prospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Mar 19;25(1):318. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07340-6. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40108490 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and risk factors of food insecurity during pregnancy: a multicenter survey in French Guiana.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 23;25(1):1910. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23173-6. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40410770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang H, Li N, Chivese T, Werfalli M, Sun H, Yuen L, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Estimation of Global and Regional Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prevalence for 2021 by International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group’s Criteria. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109050. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109050. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gomes E, Menguy C, Cahour L, Lebreton E, Regnault N et le groupe de travail sur les indicateurs en périnatalité. Rapport de surveillance de la santé périnatale en France. Santé publique France. Saint-Maurice: 2022. 159 p. Available from: www.santepubliquefrance.fr
-
- Collier A, Abraham EC, Armstrong J, Godwin J, Monteath K, Lindsay R. Reported prevalence of gestational diabetes in Scotland: The relationship with obesity, age, socioeconomic status, smoking and macrosomia, and how many are we missing? J Diabetes Investig. 2017;8:161–167. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12552. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ospina M, Osornio-Vargas ÁR, Nielsen CC, Crawford S, Kumar M, Aziz K, et al. Socioeconomic gradients of adverse birth outcomes and related maternal factors in rural and urban Alberta, Canada: a concentration index approach. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e033296. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033296. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous