Asterics: a simple tool for the ExploRation and Integration of omiCS data
- PMID: 37853347
- PMCID: PMC10583411
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-023-05504-9
Asterics: a simple tool for the ExploRation and Integration of omiCS data
Abstract
Background: The rapid development of omics acquisition techniques has induced the production of a large volume of heterogeneous and multi-level omics datasets, which require specific and sometimes complex analyses to obtain relevant biological information. Here, we present ASTERICS (version 2.5), a publicly available web interface for the analyses of omics datasets.
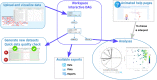
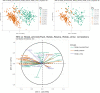
Results: ASTERICS is designed to make both standard and complex exploratory and integration analysis workflows easily available to biologists and to provide high quality interactive plots. Special care has been taken to provide a comprehensive documentation of the implemented analyses and to guide users toward sound analysis choices regarding some specific omics data. Data and analyses are organized in a comprehensive graphical workflow within ASTERICS workspace to facilitate the understanding of successive data editions and analyses leading to a given result.
Conclusion: ASTERICS provides an easy to use platform for omics data exploration and integration. The modular organization of its open source code makes it easy to incorporate new workflows and analyses by external contributors. ASTERICS is available at https://asterics.miat.inrae.fr and can also be deployed using provided docker images.
Keywords: Data integration; Omics; Statistical analyses; Web user interface.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
LB, AS, LT, and DC are all employees of the company Hyphen-Stat. The other authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
- 20008788/Région Occitanie https://www.laregion.fr/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

