Development of a novel artificial intelligence algorithm to detect pulmonary nodules on chest radiography
- PMID: 37853640
- PMCID: PMC10694515
- DOI: 10.5387/fms.2023-14
Development of a novel artificial intelligence algorithm to detect pulmonary nodules on chest radiography
Abstract
Background: In this study, we aimed to develop a novel artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm to support pulmonary nodule detection, which will enable physicians to efficiently interpret chest radiographs for lung cancer diagnosis.
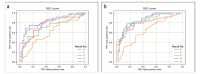
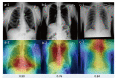
Methods: We analyzed chest X-ray images obtained from a health examination center in Fukushima and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Chest X-ray 14 dataset. We categorized these data into two types: type A included both Fukushima and NIH datasets, and type B included only the Fukushima dataset. We also demonstrated pulmonary nodules in the form of a heatmap display on each chest radiograph and calculated the positive probability score as an index value.
Results: Our novel AI algorithms had a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) area under the curve (AUC) of 0.74, a sensitivity of 0.75, and a specificity of 0.60 for the type A dataset. For the type B dataset, the respective values were 0.79, 0.72, and 0.74. The algorithms in both the type A and B datasets were superior to the accuracy of radiologists and similar to previous studies.
Conclusions: The proprietary AI algorithms had a similar accuracy for interpreting chest radiographs when compared with previous studies and radiologists. Especially, we could train a high quality AI algorithm, even with our small type B data set. However, further studies are needed to improve and further validate the accuracy of our AI algorithm.
Keywords: artificial intelligence (AI); chest radiography; deep learning; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA, 316: 2402-2410, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Grewal M, Srivastava MM, Kumar P, Varadarajan S. RADNET: Radiologist level accuracy using deep learning for hemorrhage detection in CT scans. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1710.04934, 2017.
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2010, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2010/. Accessed 14 June 2013.
-
- Horeweg N, Scholten ET, de Jong PA, et al. Detection of lung cancer through low-dose CT screening (NELSON): A prespecified analysis of screening test performance and interval cancers. Lancet Oncol, 15: 1342-1350, 2014. - PubMed

