Primary Localized Cutaneous Nodular Amyloidosis on Scalp Successfully Treated with Excision
- PMID: 37853860
- PMCID: PMC10608395
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.20.137
Primary Localized Cutaneous Nodular Amyloidosis on Scalp Successfully Treated with Excision
Abstract
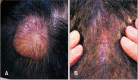
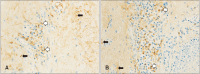
Primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis (PLCNA) is the rarest form of cutaneous amyloidosis, characterized by nodular deposits of light chain amyloids in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, without apparent systemic involvement. One or several nodules are preferably located on the extremities, trunk, or face. The most useful stain for detecting amyloid fibrils is Congo red, which, when combined with polarized light, makes amyloid proteins appear apple-green under a microscope. Immunohistochemical staining can help identify the exact type of amyloid proteins. Although the exact etiology of PLCNA is unclear, removal of nodules by shaving or surgical excision has shown good results. To the best of our knowledge, only seven cases of PLCNA have yet been reported in the Korean literature. In three of these cases, the patients had lesions on the scalp. Herein, we present a case of a 34-year-old male with PLCNA on the scalp with all the results of immunohistochemical evaluation.
Keywords: Amyloidosis; Primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis.
Copyright © The Korean Dermatological Association and The Korean Society for Investigative Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nodular amyloidosis derived from keratinocytes: an unusual type of primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis.Am J Dermatopathol. 2015 Nov;37(11):e129-33. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000307. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015. PMID: 26485243
-
Localized Cutaneous Nodular Amyloidosis in a Patient with Sjögren's Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 28;24(11):9409. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119409. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298361 Free PMC article.
-
First Case of Nodular Localized Primary Cutaneous Amyloidosis Treated With Bortezomib and Dexamethasone.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021 Jan-Dec;9:23247096211058488. doi: 10.1177/23247096211058488. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34894809 Free PMC article.
-
Primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis and CREST syndrome: a case report and review of the literature.Cutis. 2008 Jul;82(1):55-9. Cutis. 2008. PMID: 18712025 Review.
-
Primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis of the feet: a case report and review of the literature.Cutis. 2014 Feb;93(2):89-94. Cutis. 2014. PMID: 24605345 Review.
Cited by
-
A 71-year-old Woman with CREST Syndrome and Multiple Waxy Facial Papules and Plaques: A Quiz.Acta Derm Venereol. 2024 Jun 8;104:adv40419. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v104.40419. Acta Derm Venereol. 2024. PMID: 38850086 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Love WE, Miedler JD, Smith MK, Mostow EN, Cooper KD, Gilliam AC. The spectrum of primary cutaneous nodular amyloidosis: two illustrative cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(2 Suppl):S33–S35. - PubMed
-
- Huilgol SC, Ramnarain N, Carrington P, Leigh IM, Black MM. Cytokeratins in primary cutaneous amyloidosis. Australas J Dermatol. 1998;39:81–85. - PubMed
-
- Inazumi T, Hakuno M, Yamada H, Tanaka M, Naka W, Tajima S, et al. Characterization of the amyloid fibril from primary localized cutaneous nodular amyloidosis associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. Dermatology. 1994;189:125–128. - PubMed
-
- Chun HS, Chun DK, Cho KH, Eun HC, Lee YS. A case of nodular amyloidosis. Ann Dermatol. 1992;4:113–116.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

