Refractory Bullous Pemphigoid Successfully Treated with Reslizumab: A Possible Novel Therapeutic Modality
- PMID: 37853878
- PMCID: PMC10608355
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.21.177
Refractory Bullous Pemphigoid Successfully Treated with Reslizumab: A Possible Novel Therapeutic Modality
Abstract
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a chronic, autoimmune blistering disease that has concerning morbidity and mortality rates. Recently, several studies have focused on eosinophils due to their significant role in the pathogenesis of BP, considering that they are ubiquitous in the serum, tissue, and blister fluids of patients with BP. With this context, precision therapy that targets mediators of eosinophil activity could be a possible novel therapeutic strategy. Interleukin (IL)-5 is crucial for B-cell maturation, which consequently results in immunoglobulin production, and promotes eosinophil differentiation, proliferation, and activation. To our best knowledge, reslizumab has not yet been reported to treat BP. Herein, we report a case of steroid- and omalizumab-resistant BP treated successfully using reslizumab. Our data suggest that IL-5 could be a novel specific biologic target within the entire immunopathogenesis of BP, and reslizumab would be a novel therapeutic modality.
Keywords: Bullous pemphigoid; Eosinophils; Interleukin-5; Reslizumab.
Copyright © The Korean Dermatological Association and The Korean Society for Investigative Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

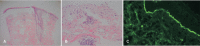
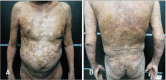
Similar articles
-
Successful induction treatment of bullous pemphigoid using reslizumab: a case report.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2021 Nov 16;17(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13223-021-00619-1. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34784964 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Disease Control in First-Line Therapy-Resistant Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and Bullous Pemphigoid with Omalizumab as Add-On Therapy: A Case Series Of 13 Patients.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 20;13:874108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.874108. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35514989 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophils in bullous pemphigoid.Panminerva Med. 2021 Sep;63(3):368-378. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.20.03997-X. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Panminerva Med. 2021. PMID: 32536149 Review.
-
A case of bullous pemphigoid developing under treatment with benralizumab for bronchial asthma.J Dermatol. 2023 Sep;50(9):1199-1202. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16811. Epub 2023 Apr 30. J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37122191
-
Targeting interleukin 4 and interleukin 13: a novel therapeutic approach in bullous pemphigoid.Ann Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):1156-1170. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2188487. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 36999962 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus proteases trigger eosinophil-mediated skin inflammation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 6;121(6):e2309243121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2309243121. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38289950 Free PMC article.
-
JAK-STAT pathway, type I/II cytokines, and new potential therapeutic strategy for autoimmune bullous diseases: update on pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1563286. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1563286. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40264772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Simon D, Borradori L, Simon HU. Eosinophils as putative therapeutic targets in bullous pemphigoid. Exp Dermatol. 2017;26:1187–1192. - PubMed
-
- Kremer N, Snast I, Cohen ES, Hodak E, Mimouni D, Lapidoth M, et al. Rituximab and omalizumab for the treatment of bullous pemphigoid: a systematic review of the literature. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Kouro T, Takatsu K. IL-5- and eosinophil-mediated inflammation: from discovery to therapy. Int Immunol. 2009;21:1303–1309. - PubMed
-
- Takatsu K. Interleukin 5 and B cell differentiation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1998;9:25–35. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

