A Critical Review of Data Science Applications in Resource Recovery and Carbon Capture from Organic Waste
- PMID: 37854077
- PMCID: PMC10580293
- DOI: 10.1021/acsestengg.3c00043
A Critical Review of Data Science Applications in Resource Recovery and Carbon Capture from Organic Waste
Abstract
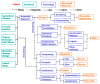
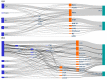
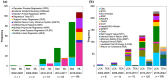
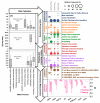
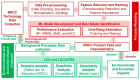
Municipal and agricultural organic waste can be treated to recover energy, nutrients, and carbon through resource recovery and carbon capture (RRCC) technologies such as anaerobic digestion, struvite precipitation, and pyrolysis. Data science could benefit such technologies by improving their efficiency through data-driven process modeling along with reducing environmental and economic burdens via life cycle assessment (LCA) and techno-economic analysis (TEA), respectively. We critically reviewed 616 peer-reviewed articles on the use of data science in RRCC published during 2002-2022. Although applications of machine learning (ML) methods have drastically increased over time for modeling RRCC technologies, the reviewed studies exhibited significant knowledge gaps at various model development stages. In terms of sustainability, an increasing number of studies included LCA with TEA to quantify both environmental and economic impacts of RRCC. Integration of ML methods with LCA and TEA has the potential to cost-effectively investigate the trade-off between efficiency and sustainability of RRCC, although the literature lacked such integration of techniques. Therefore, we propose an integrated data science framework to inform efficient and sustainable RRCC from organic waste based on the review. Overall, the findings from this review can inform practitioners about the effective utilization of various data science methods for real-world implementation of RRCC technologies.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Creegan E. F.; Flynn R.; Torell G.; Brewer C. E.; VanLeeuwen D.; Acharya R. N.; Heerema R. J.; Darapuneni M. Pecan (Carya Illinoinensis) and Dairy Waste Stream Utilization: Properties and Economics of On-Farm Windrow Systems. Sustainability 2022, 14 (5), 2550. 10.3390/su14052550. - DOI
-
- Brenes-Peralta L.; Jiménez-Morales M. F.; Campos-Rodríguez R.; Brenes-Peralta L.; Jiménez-Morales M. F.; Campos-Rodríguez R.. Food Waste Valorization through Composting and Bio-Drying for Small Scale Fruit Processing Agro-Industries. Ing. Compet. 2021, 23 ( (1), ). 10.25100/iyc.v23i1.9623. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
