Noninvasive transcutaneous bilirubin measurement in adults using skin diffuse reflectance
- PMID: 37854578
- PMCID: PMC10581810
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.500833
Noninvasive transcutaneous bilirubin measurement in adults using skin diffuse reflectance
Abstract
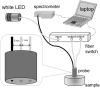
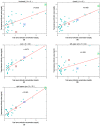
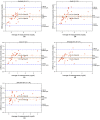
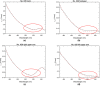
Accurate measurement of bilirubin concentration in adults is crucial for the diagnosis and management of liver and biliary tract diseases. Traditional methods relying on central laboratory testing pose challenges such as invasiveness, patient discomfort, and time consumption. Non-invasive alternatives have been explored, but their applicability to adult populations remains uncertain. This study aimed to develop and validate a portable non-invasive optical system based on spatially resolved diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) specifically tailored for adult transcutaneous bilirubin measurement. Forty-two adult patients with various underlying conditions were included in the study. Comparisons between transcutaneous bilirubin values measured by the DRS system and total serum bilirubin concentrations obtained through blood tests revealed strong correlations, particularly at the neck (r = 0.872) and the medial side of the right upper arm (r = 0.940). Bland-Altman analyses demonstrated substantial agreement between the transcutaneous bilirubin values and total serum bilirubin concentrations. The results highlight the potential of the non-invasive DRS system as a convenient and reliable tool for monitoring bilirubin values in adults.
© 2023 Optica Publishing Group under the terms of the Optica Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Evaluation of transcutaneous bilirubin measurement and agreement with bilirubinemia].Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2006 Nov-Dec;64(6):575-9. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2006. PMID: 17162260 French.
-
Transcutaneous bilirubin measurement: evaluation of Bilitest.Neonatology. 2008;93(2):101-5. doi: 10.1159/000107351. Epub 2007 Aug 16. Neonatology. 2008. PMID: 17703104
-
A Novel Non-invasive Technique of Measuring Bilirubin Levels Using BiliCapture.Oman Med J. 2019 Jan;34(1):26-33. doi: 10.5001/omj.2019.05. Oman Med J. 2019. PMID: 30671181 Free PMC article.
-
Transcutaneous bilirubinometry: its role in the assessment of neonatal jaundice.Clin Biochem. 1997 Feb;30(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(96)00131-2. Clin Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9056103 Review.
-
Noninvasive measurements of bilirubin in the newborn.Clin Perinatol. 1990 Jun;17(2):417-35. Clin Perinatol. 1990. PMID: 2196138 Review.
References
-
- GBD 2017 Cirrhosis Collaborators , “The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017,” Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 5(3), 245–266 (2020).10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ouyang G., Liu Q., Wu Y., Liu Z., Lu W., Li S., Pan G., Chen X., “The global, regional, and national burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories, 1990 to 2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017,” Cancer 127(13), 2238–2250 (2021).10.1002/cncr.33476 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
