Non-capsulated Neisseria meningitidis sepsis in a paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria patient treated with ravulizumab: case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 37854608
- PMCID: PMC10580757
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1269325
Non-capsulated Neisseria meningitidis sepsis in a paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria patient treated with ravulizumab: case report and review of the literature
Abstract
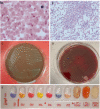
Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare acquired haematopoietic stem cell disease characterized by complement-mediated intravascular hemolysis, thrombosis, and bone marrow failure. Eculizumab and ravulizumab are anti-C5 monoclonal antibodies that reduce hemolysis, anaemia and thrombotic risk, but are associated with increased risk of infection with encapsulated bacteria, including Neisseria meningitidis. We report a case of life-threatening infection by non-groupable Neisseria meningitidis in a young PNH patient treated with ravulizumab. Despite prompt admission to the intensive care unit, microbe isolation was delayed due to the negativity of capsular antigens, and the patient required intubation, dialysis, and transfusion support for pancytopenia. Notably, PNH disease activity remained controlled and no additional anti-C5 doses were administered. Increasing awareness regarding septic risk in PNH patients on complement inhibitors despite vaccinations is pivotal. A warning about serotypes generally not pathogenetic and not covered by vaccination, such as non-capsulated forms, is emerging.
Keywords: Neisseria meningitides; eculizumab; paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria; proximal complement inhibitors; ravulizumab.
Copyright © 2023 Galli, Pettine, Panigada, Daprai, Suriano, Grancini, Barcellini and Fattizzo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

