Development of a multiassay algorithm (MAA) to identify recent HIV infection in newly diagnosed individuals in Indonesia
- PMID: 37854696
- PMCID: PMC10579430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107986
Development of a multiassay algorithm (MAA) to identify recent HIV infection in newly diagnosed individuals in Indonesia
Abstract
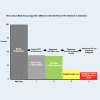
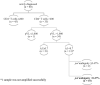
Ongoing HIV transmission is a public health priority in Indonesia. We developed a new multiassay algorithm (MAA) to identify recent HIV infection. The MAA is a sequential decision tree based on multiple biomarkers, starting with CD4+ T cells >200/μL, followed by plasma viral load (pVL) > 1,000 copies/ml, avidity index (AI) < 0 · 7, and pol ambiguity <0 · 47%. Plasma from 140 HIV-infected adults from 19 hospitals across Indonesia (January 2018 - June 2020) was studied, consisting of a training set (N = 60) of longstanding infection (>12-month) and a test set (N = 80) of newly diagnosed (≤1-month) antiretroviral (ARV) drug naive individuals. Ten of eighty (12 · 5%) newly diagnosed individuals were classified as recent infections. Drug resistance mutations (DRMs) against reverse transcriptase inhibitors were identified in two individuals: one infected with HIV subtype C (K219Q, V179T) and the other with CRF01_AE (V179D). Ongoing HIV transmission, including infections with DRMs, is substantial in Indonesia.
Keywords: Computer science; Health sciences; Medicine.
© 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Joint_United_Nations_Programme_on_HIV/AIDS_(UNAIDS) 2021. UNAIDS Data 2021.
-
- World_Health_Organization_(WHO) 2011. When and How to Use Assays for Recent Infection to Estimate HIV Incidence at a Population Level.
-
- Huik K., Soodla P., Pauskar M., Owen S.M., Luo W., Murphy G., Jõgeda E.L., Kallas E., Rajasaar H., Avi R., et al. The concordance of the limiting antigen and the Bio-Rad avidity assays in persons from Estonia infected mainly with HIV-1 CRF06_cpx. PLoS One. 2019;14 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karatzas-Delgado E.F., Ruiz-González V., García-Cisneros S., Olamendi-Portugal M.L., Herrera-Ortiz A., López-Gatell H., González-Rodríguez A., Sánchez-Alemán M.A. Evaluation of an HIV recent infection testing algorithm withserological assays among men who have sex with men in Mexico. J. Infect. Public Health. 2020;13:509–513. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

