Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37856106
- PMCID: PMC10587824
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.4423
Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Importance: Combining immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) with chemotherapy improves outcomes in patients with metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) adenocarcinoma; however, whether this combination has activity in the perioperative setting remains unknown.
Objective: To evaluate the safety and preliminary activity of perioperative chemotherapy and ICB followed by maintenance ICB in resectable G/GEJ adenocarcinoma.
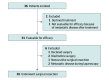
Design, setting, and participants: This investigator-initiated, multicenter, open-label, single-stage, phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial screened 49 patients and enrolled 36 patients with resectable G/GEJ adenocarcinoma from February 10, 2017, to June 17, 2021, with a median (range) follow-up of 35.2 (17.4-73.0) months. Thirty-four patients were deemed evaluable for efficacy analysis, with 28 (82.4%) undergoing curative resection. This study was performed at 4 referral institutions in the US.
Interventions: Patients received 3 cycles of capecitabine, 625 mg/m2, orally twice daily for 21 days; oxaliplatin, 130 mg/m2, intravenously and pembrolizumab, 200 mg, intravenously with optional epirubicin, 50 mg/m2, every 3 weeks before and after surgery with an additional cycle of pembrolizumab before surgery. Patients received 14 additional doses of maintenance pembrolizumab.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was pathologic complete response (pCR) rate. Secondary end points included overall response rate, disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS), and safety.
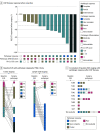
Results: A total of 34 patients (median [range] age, 65.5 [25-90] years; 23 [67.6%] male) were evaluable for efficacy. Of these patients, 28 (82.4%) underwent curative resection, 7 (20.6%; 95% CI, 10.1%-100%) achieved pCR, and 6 (17.6%) achieved a pathologic near-complete response. Of the 28 patients who underwent resection, 4 (14.3%) experienced disease recurrence. The median DFS and OS were not reached. The 2-year DFS was 67.8% (95% CI, 0.53%-0.87%) and the OS was 80.6% (95% CI, 0.68%-0.96%). Treatment-related grade 3 or higher adverse events for evaluable patients occurred in 20 patients (57.1%), and 12 (34.3%) experienced immune-related grade 3 or higher adverse events.
Conclusion and relevance: In this trial of unselected patients with resectable G/GEJ adenocarcinoma, capecitabine, oxaliplatin, and pembrolizumab resulted in a pCR rate of 20.6% and was well tolerated. This trial met its primary end point and supports the development of checkpoint inhibition in combination with perioperative chemotherapy in locally advanced G/GEJ adenocarcinoma.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02918162.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Al-Batran SE, Homann N, Pauligk C, et al. ; FLOT4-AIO Investigators . Perioperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel versus fluorouracil or capecitabine plus cisplatin and epirubicin for locally advanced, resectable gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (FLOT4): a randomised, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10184):1948-1957. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32557-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shitara K, Van Cutsem E, Bang Y-J, et al. . Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab or pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone for patients with first-line, advanced gastric cancer: the KEYNOTE-062 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(10):1571-1580. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.3370 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fuchs CS, Doi T, Jang RW, et al. . Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with previously treated advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer: phase 2 clinical KEYNOTE-059 trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(5):e180013-e180013. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

