Webcast marketing platform optimization via 6G R&D and the impact on brand content creation
- PMID: 37856448
- PMCID: PMC10586639
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292394
Webcast marketing platform optimization via 6G R&D and the impact on brand content creation
Abstract
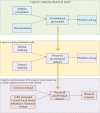
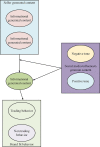
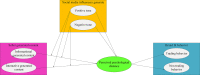
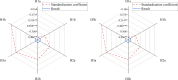
This work aims to investigate the development and management of cosmetics webcast marketing platforms, offering novel approaches for building and sustaining commercial brands. Firstly, an analysis of the current utilization of cosmetics webcast marketing platforms is conducted, identifying operational challenges associated with these platforms. Secondly, optimization strategies are proposed to address the identified issues by leveraging advancements in 6th Generation (6G) communication technology. Subsequently, a conceptual framework is established, employing big data interaction to examine the influence of webcast marketing platform experiences on brand fit. Multiple hypotheses are formulated to explore the relationship between platform experiences and brand fit. Finally, empirical analysis is performed within the context of the 5th Generation (5G) Mobile Communication Technology and extended to incorporate the 6G Mobile Communication Technology landscape. The results of the validation indicate the following: (1) the content generated by the webcast marketing platform has a positive impact on brand fit (β = 0.46, p<0.01; β = 0.31, p<0.05); (2) in the 6G network environment, a webcast marketing platform with high traffic transmission rates may enhance brand fit (β = 0.51, p<0.001); (3) the content generated by the webcast marketing platform exhibits significant positive regulatory effects on information-based and co-generated content (β = 0.42, p<0.01; β = 0.02, p<0.001). The findings of this work offer valuable insights for other scholars and researchers seeking to optimize webcast marketing platforms.
Copyright: © 2023 Hui Wen. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Yuan CH, Wu Y J. Mobile instant messaging or face-to-face? Group interactions in cooperative simulations. COMPUT HUM BEHAV, 2020; 113:106508.
-
- Zhao Y, Lu P, Chen W. Research on Chinese live broadcast marketing and sustainable consumption intention under the internet environment. JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY DESIGN CULTURE, 2022; 11:106–109.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

