Structure of human TRPM8 channel
- PMID: 37857704
- PMCID: PMC10587237
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-05425-6
Structure of human TRPM8 channel
Abstract
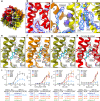
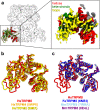
TRPM8 is a non-selective cation channel permeable to both monovalent and divalent cations that is activated by multiple factors, such as temperature, voltage, pressure, and changes in osmolality. It is a therapeutic target for anticancer drug development, and its modulators can be utilized for several pathological conditions. Here, we present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of a human TRPM8 channel in the closed state that was solved at 2.7 Å resolution. Our structure comprises the most complete model of the N-terminal pre-melastatin homology region. We also visualized several lipids that are bound by the protein and modeled how the human channel interacts with icilin. Analyses of pore helices in available TRPM structures showed that all these structures can be grouped into different closed, desensitized and open state conformations based on the register of the pore helix S6 which positions particular amino acid residues at the channel constriction.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. Supplementary Information is available for this paper. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Carmine Talarico or Marcin Nowotny.
Figures


References
-
- Voets, T., Owsianik, G. & Nilius, B. TRPM8. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol.222, 329–344 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

