Sepsis‑induced cardiac dysfunction and pathogenetic mechanisms (Review)
- PMID: 37859613
- PMCID: PMC10619129
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13114
Sepsis‑induced cardiac dysfunction and pathogenetic mechanisms (Review)
Abstract
Sepsis is a manifestation of the immune and inflammatory response to infection, which may lead to multi‑organ failure. Health care advances have improved outcomes in critical illness, but it still remains the leading cause of death. Septic cardiomyopathy is heart dysfunction brought on by sepsis. Septic cardiomyopathy is a common consequence of sepsis and has a mortality rate of up to 70%. There is a lack of understanding of septic cardiomyopathy pathogenesis; knowledge of its pathogenesis and the identification of potential therapeutic targets may reduce the mortality rate of patients with sepsis and lead to clinical improvements. The present review aimed to summarize advances in the pathogenesis of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis, with a focus on mitochondrial dysfunction, metabolic changes and cell death modalities and pathways. The present review summarized diagnostic criteria and outlook for sepsis treatment, with the goal of identifying appropriate treatment methods for this disease.
Keywords: ferroptosis; metabolic change; mitochondrial dysfunction; sepsis; signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
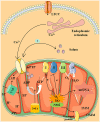
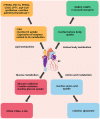
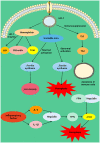
References
-
- Hammond N, Kumar A, Kaur P, Tirupakuzhi Vijayaraghavan BK, Ghosh A, Grattan S, Jha V, Mathai D, Venkatesh B, Sepsis in India Prevalence Study (SIPS) Investigator Network Estimates of sepsis prevalence and outcomes in adult patients in the ICU in India: A cross-sectional Study. Chest. 2022;161:1543–1554. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2021.12.673. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shankar-Hari M, Phillips G, Levy ML, Seymour CW, Liu VX, Deutschman CS, Angus DC, Rubenfeld GD, Singer M, Sepsis Definitions Task Force Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: For the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:775–787. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0289. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM consensus conference committee. American college of chest physicians/society of critical care medicine. Chest. 1992;101:1644–1655. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644. - DOI - PubMed

