Licochalcone A induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via suppressing MAPK signaling pathway and the expression of FBXO5 in lung squamous cell cancer
- PMID: 37859622
- PMCID: PMC10620845
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2023.8651
Licochalcone A induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via suppressing MAPK signaling pathway and the expression of FBXO5 in lung squamous cell cancer
Abstract
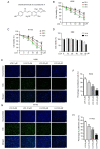
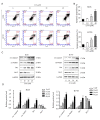
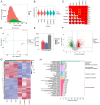
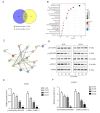
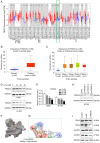
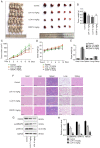
Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) is a highly heterogeneous malignancy with high mortality and few therapeutic options. Licochalcone A (LCA, PubChem ID: 5318998) is a chalcone extracted from licorice and possesses anticancer and anti‑inflammatory activities. The present study aimed to elucidate the anticancer effect of LCA on LSCC and explore the conceivable molecular mechanism. MTT assay revealed that LCA significantly inhibited the proliferation of LSCC cells with less cytotoxicity towards human bronchial epithelial cells. 5‑ethynyl‑2'‑deoxyuridine (EdU) assay demonstrated that LCA could reduce the proliferation rate of LSCC cells. The flow cytometric assays indicated that LCA increased the cell number of the G1 phase and induced the apoptosis of LSCC cells. LCA downregulated the protein expression of cyclin D1, cyclin E, CDK2 and CDK4. Meanwhile, LCA increased the expression level of Bax, cleaved poly(ADP‑ribose)polymerase‑1 (PARP1) and caspase 3, as well as downregulated the level of Bcl‑2. Proteomics assay demonstrated that LCA exerted its antitumor effects via inhibiting mitogen‑activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways and the expression of F‑box protein 5 (FBXO5). Western blot analysis showed that LCA decreased the expression of p‑ERK1/2, p‑p38MAPK and FBXO5. In the xenograft tumors of LSCC, LCA significantly inhibited the volumes and weight of tumors in nude mice with little toxicity in vital organs. Therefore, the present study demonstrated that LCA effectively inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in vitro, and suppressed xenograft tumor growth in vivo. LCA may serve as a future therapeutic candidate of LSCC.
Keywords: F‑box protein 5; apoptosis; licochalcone A; lung squamous cell carcinoma; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

