Anti-Arthritis Effect of Ethanol Extract of Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) Leaves Against Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Model in Mice
- PMID: 37860100
- PMCID: PMC10583854
- DOI: 10.21315/tlsr2023.34.3.13
Anti-Arthritis Effect of Ethanol Extract of Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) Leaves Against Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Model in Mice
Abstract
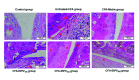
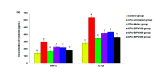
Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) is a well-known oleaginous plant used as food source and traditional medicine by indigenous people for a long time. This study was conducted to evaluate anti-arthritis effect of ethanol extract of Sacha inchi leaves and provide scientific evidence to develop the new anti-arthritis remedy from Sacha inchi. Rheumatoid arthritis model was established by injection of complete Freund's adjuvant into right hind footpads of mice and three doses of ethanol extract of Sacha inchi leaves (100, 200 and 300 mg/kg body weight) were used for treatment. The severity of arthritis was evaluated by measuring the ankle diameter and arthritic score, hematological and biochemical parameters (erythrocytes, leukocytes, lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes counts, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein and rheumatoid factor). The pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, INF-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10) and the histology change of joint were also examined. All three doses of extracts significantly alleviated ankle diameter and arthritic score. Furthermore, the extracts could ameliorate the alternation of inflammatory cytokines as well histological features of CFA-induced mice. The efficacy of extract dose of 300 mg/kg body weight is comparable with reference drug (Mobic, 0.2 mg/kg body weight). This study indicates Sacha inchi leaf extract as the promising remedy for treatment of arthritis.
Keywords: Animal Model; Anti-Arthritis Effect; Antioxidants; Inflammatory Cytokines; Plukenetia volubilis.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2023.
Figures





References
-
- Abdisa Z, Kenea F. Phytochemical screening, antibacterial and antioxidant activity studies on the crude root extract of Clematis hirsuta. Cogent Chemistry. 2020;6:1. doi: 10.1080/23312009.2020.1862389. - DOI
-
- Ambriz-Pérez DL, Leyva-López N, Gutiérrez-Grijalva EP, Heredia JB. Phenolic compounds: Natural alternative in inflammation treatment: A review. Cogent Food & Agriculture. 2016;2:1131412. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2015.1131412. - DOI
-
- Ambulay JP, Rojas PA, Timoteo OS, Barreto TV, Colarossi A. Effect of the emulsion of Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia huayabambana) oil on oxidative stress and inflammation in rats induced to obesity. Journal of Functional Foods. 2020;64:103631. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103631. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
