Transfer from continuous to discrete quantities in honeybees
- PMID: 37860770
- PMCID: PMC10582340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108035
Transfer from continuous to discrete quantities in honeybees
Abstract
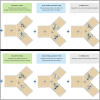
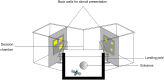
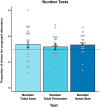
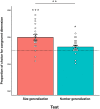
Honeybees can estimate quantities having different dimensions: continuous and uncountable such as the relative size of visual objects in an array, or discrete and countable such as the number of objects of the array. Honeybees can transfer quantity discrimination (i.e., choosing the larger/smaller stimulus) from number to size. Here, we investigated whether honeybees could also generalize from the size (continuous) to the number (discrete) dimension. We trained free-flying foragers to discriminate between large- and small-size elements. At test, bees were presented with a comparison between larger and smaller numerosities controlled for different continuous variables covarying with numerosity such as total area, total perimeter, convex hull, and element size. Results showed that bees generalized from the size to the numerical dimension of the stimuli. This cross-dimensional transfer supports the idea of a universal mechanism for the encoding of abstract magnitudes in invertebrate species comparable to that of vertebrate species.
Keywords: Behavioral neuroscience; Biological sciences; Natural sciences.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Walsh V. In: The Oxford Handbook of Numerical Cognition. Cohen Kadosh R., Dowker A., editors. Oxford Library Of Psychology; 2015. A Theory Of Magnitude: the parts that sum to number; pp. 552–565.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

