The Indian registry on current patient profiles & treatment trends in hypertension (RECORD): One year interim analysis
- PMID: 37861623
- PMCID: PMC10720968
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_3096_21
The Indian registry on current patient profiles & treatment trends in hypertension (RECORD): One year interim analysis
Abstract
Background & objectives: In India, hypertension constitutes a significant health burden. This observational, non-interventional, prospective study was conducted in five centres across India to evaluate the current clinical practices for the management of hypertension.
Methods: Participants were enrolled if they were newly diagnosed with essential hypertension or had pre-existing hypertension and were on the same therapeutic plan for the previous three months. At baseline, three months, six months, and one year, information on the patient and their treatment regimen was documented, and their quality of life (QoL) was evaluated.
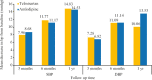
Results: A total of 2000 individuals were enrolled in this study, with a mean age of 54.45 yr. Of these, 55.7 per cent (n=1114) were males, and 957 (47.85%) were newly diagnosed with hypertension, while 1043 (52.15%) had pre-existing hypertension. Stage 2 hypertension (systolic blood pressure (BP) >140 or diastolic BP ≥90 mmHg) accounted for more than 70 per cent of the participants (70.76% of pre-existing and 76.29% of newly diagnosed); the average duration of pre-existing hypertension was 68.72 months. Diabetes (31.6%) and dyslipidaemia (15.8%) were the most common comorbidities. In 43.3 per cent of the participants, monotherapy was used, and in 56.7 per cent (70.55% fixed-dose combination), combination therapy was used. Telmisartan (31.6%), amlodipine (35.2%), and a combination of the two (27.1%) were the most commonly prescribed treatment regimens. At three months, six months, and one year, treatment modifications were observed in 1.4, 1.05, and 0.23 per cent of the participants receiving monotherapy and 2.74, 4.78 and 0.35 per cent receiving combination therapy, respectively. In both groups, the proportion of individuals with controlled hypertension (≤140/90 mmHg) increased by more than 30 per cent after a year. At one year, physical and emotional role functioning, social functioning, and health improved considerably.
Interpretation & conclusions: Combination therapy for hypertension is increasingly preferred at the time of initial diagnosis. The efficacy, safety, and tolerance of the recommended medications were reflected by improvements in the QoL and the minimal changes in the therapeutic strategy required.
Keywords: Amlodipine; India; combination therapy; fixed-dose combination; hypertension; monotherapy; registry; telmisartan; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The study was sponsored by Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd. across five sites in India. Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd. claims no authorship in the publication and is available to clarify in the event of any disputes in this context.The part of the study was presented in 73rd Annual Conference of Cardiological Society of India (CSI), 2021 and the abstract was published in the
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Indian REgistry on Current Patient PrOfiles and TReatment TrenDs in Hypertension (RECORD): Final Outcomes of the Real-world Observational Study.J Assoc Physicians India. 2023 Nov;71(11):43-49. doi: 10.59556/japi.71.0399. J Assoc Physicians India. 2023. PMID: 38720496
-
Management of hypertension with the fixed combination of perindopril and amlodipine in daily clinical practice: results from the STRONG prospective, observational, multicenter study.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009;9(3):135-42. doi: 10.1007/BF03256570. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19463019 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness and tolerability of fixed-dose combination enalapril plus nitrendipine in hypertensive patients: results of the 3-month observational, post-marketing, multicentre, prospective CENIT study.Clin Drug Investig. 2009;29(7):459-469. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200929070-00004. Clin Drug Investig. 2009. PMID: 19499963
-
Single-pill telmisartan and amlodipine: a rational combination for the treatment of hypertension.Drugs. 2011 Dec 3;71(17):2295-305. doi: 10.2165/11594510-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 22085386 Review.
-
Review: a single-pill combination of telmisartan plus amlodipine for the treatment of hypertension.Postgrad Med. 2011 Nov;123(6):58-65. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2011.11.2495. Postgrad Med. 2011. PMID: 22104454 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Fact sheet-Hypertension; 2019. [accessed on October 29, 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension#:~:text=Hy... .
-
- Gopalakrishnan S, Rama R, Savitha AK. Determinants of hypertension among urban adult population in Kancheepuram district of Tamil Nadu determinants of hypertension among urban adult population in Kancheepuram district of Tamil Nadu. IJCMPH. 2017;4:1552–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical