Phase III, Randomized Study of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy in Patients With EGFR- or ALK-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ATTLAS, KCSG-LU19-04)
- PMID: 37861993
- PMCID: PMC11095857
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.01891
Phase III, Randomized Study of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy in Patients With EGFR- or ALK-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ATTLAS, KCSG-LU19-04)
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Phase III, Randomized Study of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy in Patients With EGFR- or ALK-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ATTLAS, KCSG-LU19-04).J Clin Oncol. 2024 Aug 1;42(22):2725. doi: 10.1200/JCO.24.01092. Epub 2024 Jun 17. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38885462 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: In the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a driver mutation, the role of anti-PD-(L)1 antibody after tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) remains unclear. This randomized, open-label, multicenter, phase III study evaluates the efficacy of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin (ABCP ) in EGFR- or ALK-mutated NSCLC that progressed before TKI therapy.
Materials and methods: We compared the clinical efficacy of ABCP followed by maintenance therapy with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab with pemetrexed plus carboplatin or cisplatin (PC) followed by pemetrexed maintenance. The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS).
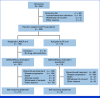
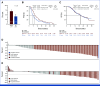
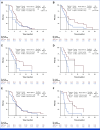
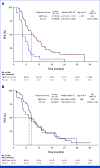
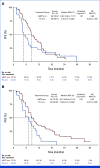
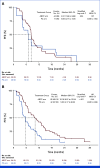
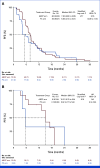
Results: A total of 228 patients with activating EGFR mutation (n = 215) or ALK translocation (n = 13) were enrolled from 16 sites in the Republic of Korea and randomly assigned at 2:1 ratio to either ABCP (n = 154) or PC arm (n = 74). The median follow-up duration was 26.1 months (95% CI, 24.7 to 28.2). Objective response rates (69.5% v 41.9%, P < .001) and median PFS (8.48 v 5.62 months, hazard ratio [HR], 0.62 [95% CI, 0.45 to 0.86]; P = .004) were significantly better in the ABCP than PC arm. PFS benefit increased as PD-L1 expression increased, with an HR of 0.47, 0.41, and 0.24 for PD-L1 ≥1%, ≥10%, and ≥50%, respectively. Overall survival was similar between ABCP and PC arm (20.63 v 20.27 months, HR, 1.01 [95% CI, 0.69 to 1.46]; P = .975). The safety profile of the ABCP arm was comparable with that previously reported, with no additional safety signals, but higher rates of treatment-related adverse events were observed compared with the PC arm.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this study is the first randomized phase III study to demonstrate the clinical benefit of anti-PD-L1 antibody in combination with bevacizumab and chemotherapy in patients with EGFR- or ALK-mutated NSCLC who have progressed on relevant targeted therapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03991403.
Conflict of interest statement
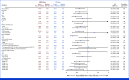
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures



References
-
- Singh N, Temin S, Baker S, et al. Therapy for stage IV non–small-cell lung cancer with driver alterations: ASCO living guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:3310–3322. - PubMed
-
- Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, et al. Overall survival with Osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:41–50. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Bauer TM, De Marinis F, et al. First-line lorlatinib or crizotinib in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2018–2029. - PubMed
-
- Peters S, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:829–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

