An essential role for miR-15/16 in Treg suppression and restriction of proliferation
- PMID: 37862171
- PMCID: PMC10664750
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113298
An essential role for miR-15/16 in Treg suppression and restriction of proliferation
Abstract
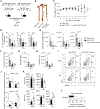
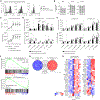
The miR-15/16 family targets a large network of genes in T cells to restrict their cell cycle, memory formation, and survival. Upon T cell activation, miR-15/16 are downregulated, allowing rapid expansion of differentiated effector T cells to mediate a sustained response. Here, we used conditional deletion of miR-15/16 in regulatory T cells (Tregs) to identify immune functions of the miR-15/16 family in T cells. miR-15/16 are indispensable to maintain peripheral tolerance by securing efficient suppression by a limited number of Tregs. miR-15/16 deficiency alters expression of critical Treg proteins and results in accumulation of functionally impaired FOXP3loCD25loCD127hi Tregs. Excessive proliferation in the absence of miR-15/16 shifts Treg fate and produces an effector Treg phenotype. These Tregs fail to control immune activation, leading to spontaneous multi-organ inflammation and increased allergic inflammation in a mouse model of asthma. Together, our results demonstrate that miR-15/16 expression in Tregs is essential to maintain immune tolerance.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; T cell; T regulatory cell; TCF1; Treg; allergy; effector Treg; immunosuppression; miR-15; miR-16; miRNA.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


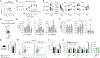


Update of
-
An essential role for miR-15/16 in Treg suppression and restriction of proliferation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 26:2023.03.26.533356. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.26.533356. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Rep. 2023 Oct 31;42(10):113298. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113298. PMID: 36993421 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

