Promising use of metformin in treating neurological disorders: biomarker-guided therapies
- PMID: 37862207
- PMCID: PMC10749596
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.385286
Promising use of metformin in treating neurological disorders: biomarker-guided therapies
Abstract
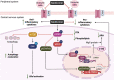
Neurological disorders are a diverse group of conditions that affect the nervous system and include neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease), cerebrovascular conditions (stroke), and neurodevelopmental disorders (autism spectrum disorder). Although they affect millions of individuals around the world, only a limited number of effective treatment options are available today. Since most neurological disorders express mitochondria-related metabolic perturbations, metformin, a biguanide type II antidiabetic drug, has attracted a lot of attention to be repurposed to treat neurological disorders by correcting their perturbed energy metabolism. However, controversial research emerges regarding the beneficial/detrimental effects of metformin on these neurological disorders. Given that most neurological disorders have complex etiology in their pathophysiology and are influenced by various risk factors such as aging, lifestyle, genetics, and environment, it is important to identify perturbed molecular functions that can be targeted by metformin in these neurological disorders. These molecules can then be used as biomarkers to stratify subpopulations of patients who show distinct molecular/pathological properties and can respond to metformin treatment, ultimately developing targeted therapy. In this review, we will discuss mitochondria-related metabolic perturbations and impaired molecular pathways in these neurological disorders and how these can be used as biomarkers to guide metformin-responsive treatment for the targeted therapy to treat neurological disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; metformin; mitochondrial perturbation; multiple sclerosis; neural degenerative diseases; stroke; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures



References
-
- Abd-Elsameea AA, Moustaf AA, Mohamed AM. Modulation of the oxidative stress by metformin in the cerebrum of rats exposed to global cerebral ischemia and ischemia/reperfusion. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2014);18:2387–2392. - PubMed
-
- Abdi M, Pasbakhsh P, Shabani M, Nekoonam S, Sadeghi A, Fathi F, Abouzaripour M, Mohamed W, Zibara K, Kashani IR, Zendedel A. Metformin therapy attenuates pro-inflammatory microglia by inhibiting NF-κB in cuprizone demyelinating mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Neurotox Res. (2021);39:1732–1746. - PubMed
-
- Adedeji HA, Ishola IO, Adeyemi OO. Novel action of metformin in the prevention of haloperidol-induced catalepsy in mice:potential in the treatment of Parkinson's disease? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2014);48:245–251. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi S, Razazan A, Nagpal R, Jain S, Wang B, Mishra SP, Wang S, Justice J, Ding J, McClain DA, Kritchevsky SB, Kitzman D, Yadav H. Metformin reduces aging-related leaky gut and improves cognitive function by beneficially modulating gut microbiome/goblet cell/mucin axis. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2020);75:e9–21. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

