Mechanosensing by Vascular Endothelium
- PMID: 37863105
- PMCID: PMC10922104
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-042022-030946
Mechanosensing by Vascular Endothelium
Abstract
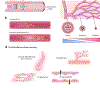
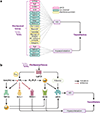
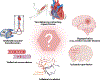
Mechanical forces influence different cell types in our bodies. Among the earliest forces experienced in mammals is blood movement in the vascular system. Blood flow starts at the embryonic stage and ceases when the heart stops. Blood flow exposes endothelial cells (ECs) that line all blood vessels to hemodynamic forces. ECs detect these mechanical forces (mechanosensing) through mechanosensors, thus triggering physiological responses such as changes in vascular diameter. In this review, we focus on endothelial mechanosensing and on how different ion channels, receptors, and membrane structures detect forces and mediate intricate mechanotransduction responses. We further highlight that these responses often reflect collaborative efforts involving several mechanosensors and mechanotransducers. We close with a consideration of current knowledge regarding the dysregulation of endothelial mechanosensing during disease. Because hemodynamic disruptions are hallmarks of cardiovascular disease, studying endothelial mechanosensing holds great promise for advancing our understanding of vascular physiology and pathophysiology.
Keywords: G protein–coupled receptors; Piezo1; endothelial cells; ion channels; mechanosensing; mechanosensors; mechanotransduction; shear stress.
Figures

References
-
- Cecchi E, Giglioli C, Valente S, Lazzeri C, Gensini GF, et al. 2011. Role of hemodynamic shear stress in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 214(2):249–56 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

