Enhancing radiomics and Deep Learning systems through the standardization of medical imaging workflows
- PMID: 37865635
- PMCID: PMC10590396
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-023-02641-x
Enhancing radiomics and Deep Learning systems through the standardization of medical imaging workflows
Abstract
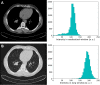
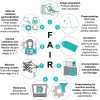
Recent advances in computer-aided diagnosis, treatment response and prognosis in radiomics and deep learning challenge radiology with requirements for world-wide methodological standards for labeling, preprocessing and image acquisition protocols. The adoption of these standards in the clinical workflows is a necessary step towards generalization and interoperability of radiomics and artificial intelligence algorithms in medical imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. Ca Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

