Computational prognostic evaluation of Alzheimer's drugs from FDA-approved database through structural conformational dynamics and drug repositioning approaches
- PMID: 37865690
- PMCID: PMC10590448
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-45347-1
Computational prognostic evaluation of Alzheimer's drugs from FDA-approved database through structural conformational dynamics and drug repositioning approaches
Abstract
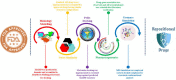
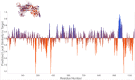
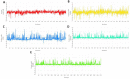
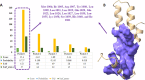
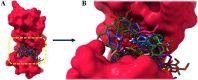
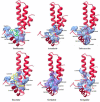
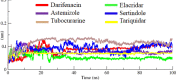
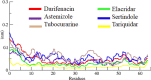
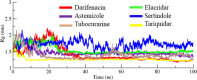
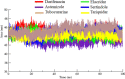
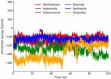
Drug designing is high-priced and time taking process with low success rate. To overcome this obligation, computational drug repositioning technique is being promptly used to predict the possible therapeutic effects of FDA approved drugs against multiple diseases. In this computational study, protein modeling, shape-based screening, molecular docking, pharmacogenomics, and molecular dynamic simulation approaches have been utilized to retrieve the FDA approved drugs against AD. The predicted MADD protein structure was designed by homology modeling and characterized through different computational resources. Donepezil and galantamine were implanted as standard drugs and drugs were screened out based on structural similarities. Furthermore, these drugs were evaluated and based on binding energy (Kcal/mol) profiles against MADD through PyRx tool. Moreover, pharmacogenomics analysis showed good possible associations with AD mediated genes and confirmed through detail literature survey. The best 6 drug (darifenacin, astemizole, tubocurarine, elacridar, sertindole and tariquidar) further docked and analyzed their interaction behavior through hydrogen binding. Finally, MD simulation study were carried out on these drugs and evaluated their stability behavior by generating root mean square deviation and fluctuations (RMSD/F), radius of gyration (Rg) and soluble accessible surface area (SASA) graphs. Taken together, darifenacin, astemizole, tubocurarine, elacridar, sertindole and tariquidar displayed good lead like profile as compared with standard and can be used as possible therapeutic agent in the treatment of AD after in-vitro and in-vivo assessment.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The exploration of novel Alzheimer's therapeutic agents from the pool of FDA approved medicines using drug repositioning, enzyme inhibition and kinetic mechanism approaches.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:2513-2526. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.115. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551512
-
Exploration of Potential Ewing Sarcoma Drugs from FDA-Approved Pharmaceuticals through Computational Drug Repositioning, Pharmacogenomics, Molecular Docking, and MD Simulation Studies.ACS Omega. 2022 Jun 1;7(23):19243-19260. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00518. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35721972 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual screening, pharmacokinetics, molecular dynamics and binding free energy analysis for small natural molecules against cyclin-dependent kinase 5 for Alzheimer's disease.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020 Jan;38(1):248-262. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2019.1571947. Epub 2019 Feb 21. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020. PMID: 30688165
-
Repurposing of FDA-approved drugs as dual-acting MAO-B and AChE inhibitors against Alzheimer's disease: An in silico and in vitro study.J Mol Graph Model. 2023 Jul;122:108471. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2023.108471. Epub 2023 Apr 14. J Mol Graph Model. 2023. PMID: 37087882 Review.
-
Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer's Disease: Multitargeting Strategy Based on Anti-Alzheimer's Drugs Repositioning.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(33):3519-3535. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191008103141. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31593530 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances and future perspectives in small molecule JAK2 inhibitors.Future Med Chem. 2025 May;17(10):1175-1191. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2025.2507564. Epub 2025 May 20. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40392133 Review.
References
-
- Acarin L, González B, Castellano B. Stat3 and NFκB glial expression after excitotoxic damage to the postnatal brain. NeuroReport. 1998;9:2869–2873. - PubMed
-
- Moustafa AA, et al. Genetic underpinnings in Alzheimer’s disease—a review. Rev. Neurosci. 2018;29:21–38. - PubMed
-
- Cutsuridis V, Moustafa AA. Neurocomputational models of Alzheimer’s disease. Scholarpedia. 2017;12:32144.
-
- Ahn KS, Aggarwal BB. Transcription factor NF-κB: A sensor for smoke and stress signals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005;1056:218–233. - PubMed
-
- Hassan M, Raza H, Abbasi MA, Moustafa AA, Seo S-Y. The exploration of novel Alzheimer’s therapeutic agents from the pool of FDA approved medicines using drug repositioning, enzyme inhibition and kinetic mechanism approaches. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019;109:2513–2526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

