The role of dysregulated ghrelin/LEAP-2 balance in anorexia nervosa
- PMID: 37867951
- PMCID: PMC10587521
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107996
The role of dysregulated ghrelin/LEAP-2 balance in anorexia nervosa
Abstract
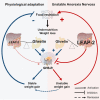
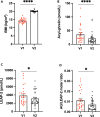
LEAP-2 is a ghrelin antagonist with an anorexigenic drive. This study investigates the evolution of plasma ghrelin and LEAP-2 concentrations in 29 patients with anorexia nervosa (AN) before and after refeeding and compares it to physiological adaptations during fasting in healthy controls or to mouse model of chronic food restriction and refeeding. Acute and chronic food restriction decrease LEAP-2 and increase ghrelin concentrations in both humans and mice, while patients with AN displayed higher ghrelin and LEAP-2 concentrations before than after refeeding (p = 0.043). After 6 months follow-up, patients with unstable weight gain (n = 17) had significantly decreased LEAP-2 concentrations after refeeding (p = 0.044), in contrast to patients with stable weight gain (n = 12). We provide evidence that the ghrelin/LEAP-2 system is not regulated according to the nutritional status in AN, in contrast to what is physiologically expected when coping with food restriction.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Endocrinology; Health sciences; Medicine; Natural sciences; Nutrition; Psychiatry.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Philip Gorwood received during the last 5 years fees for presentations at congresses or participation in scientific boards from Angelini, EISI, Janssen, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Pileje and Merk. The other authors have no interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Fifth edition. American Psychiatric Association; 2013. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
-
- Duncan L., Yilmaz Z., Gaspar H., Walters R., Goldstein J., Anttila V., Bulik-Sullivan B., Ripke S., Eating Disorders Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Thornton L., et al. Significant Locus and Metabolic Genetic Correlations Revealed in Genome-Wide Association Study of Anorexia Nervosa. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2017;174:850–858. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.16121402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

