Immune Adjuvant Therapy With Interleukin-7 in a Lymphopenic Patient With Aplastic Anemia and Mucormycosis
- PMID: 37868029
- PMCID: PMC10589520
- DOI: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000990
Immune Adjuvant Therapy With Interleukin-7 in a Lymphopenic Patient With Aplastic Anemia and Mucormycosis
Abstract
Background: We report the case of a patient with aplastic anemia and pancytopenia on immune-suppressive therapy who developed invasive pulmonary infection with mucormycosis and was treated with immune adjuvant therapy.
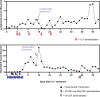
Case summary: Given the patient's profound lymphopenia and progressive invasive mucor despite dual antifungal drug therapy, interleukin (IL)-7, a cytokine that induces lymphocyte activation and proliferation, was instituted and resulted in normalization of absolute lymphocyte counts and was temporally associated with clearance of fungal pathogens and resolution of clinical symptoms.
Conclusion: Patients with life-threatening fungal infections are frequently immune suppressed and immune adjuvant therapies should be considered in patients who are not responding to antifungal drugs and source control. Well-designed, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials are needed to advance the field. Although a number of immune adjuvants may be beneficial in fungal sepsis, IL-7 is a particularly attractive immune adjuvant because of its broad immunologic effects on key immunologic pathways that mediate enhanced antifungal immune system activity.
Keywords: fungal; immunity; infection; lymphocyte; sepsis.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Hotchkiss has been an investigator on several trials of IL-7 in sepsis. The remaining authors have not disclosed any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tsay S, Williams S, Mu Y, et al.: National Burden of Candidemia, United States, 2017. Open Forum Infect Dis 2018; 5:S142–S143
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

