Using the 6-min walk test to assess the clinical response to mepolizumab and conventional therapy in severe eosinophilic asthma
- PMID: 37868145
- PMCID: PMC10588793
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00114-2023
Using the 6-min walk test to assess the clinical response to mepolizumab and conventional therapy in severe eosinophilic asthma
Abstract
Background: Severe asthma limits exercise to avoid respiratory symptoms. The objective of the present study was to investigate the role of the 6-min walk test (6MWT) in severe asthma.
Methods: Consecutive patients with severe eosinophilic asthma were enrolled. A 6MWT was performed before and after 12 months. Inhaled therapy dose, oral corticosteroids dose, pulmonary function tests, eosinophil blood count, fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO), Asthma Control Test (ACT) score and responses to the Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ) were also recorded.
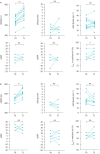
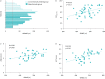
Results: Of the 22 patients enrolled, 13 were treated with mepolizumab 100 mg every 4 weeks in addition to conventional therapy and nine with conventional therapy only. The majority of the patients were treated with high-dose inhaled corticosteroids/long-acting β-agonists/long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonists, while approximately half were on continuous oral corticosteroids. After 12 months, the mepolizumab group only showed a significant improvement in pulmonary function tests (percentage forced expiratory volume in 1 s and percentage forced expiratory flow at 25-75% forced vital capacity (FEF25-75%), both p<0.001; percentage forced vital capacity, p<0.01) and clinical laboratory parameters (eosinophil count, FeNO measured at a flow rate of 50 mL·s-1, ACT and AQLQ, p<0.001). No significant changes in the proportion of patients using continuous oral corticosteroids and high-dose inhaled corticosteroids/long-acting β-agonists/long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonists were observed in either group (p>0.05). By paired comparisons, statistically significant improvements of the mean 6-min walk distance (6MWD) were observed in the mepolizumab (p<0.001) and conventional therapy (p<0.01) groups, while no improvement was seen in dyspnoea Borg scale, heart rate, percentage oxygen saturation or systolic and diastolic blood pressure. 6MWD showed significant direct correlations with ACT (r=0.5998, p<0.001), AQLQ (r=0.3978, p=0.009) and FEF25-75% (r=0.3589, p=0.017).
Conclusions: The 6MWT could complement severe asthma assessment and be relevant in evaluating the objective response to treatment, including biological therapies like mepolizumab.
Copyright ©The authors 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A case of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis successfully treated with mepolizumab.BMC Pulm Med. 2018 Mar 27;18(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0617-5. BMC Pulm Med. 2018. PMID: 29587693 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophils depletion therapy for severe asthma management following favorable response to mepolizumab.Respir Med Case Rep. 2019 Jul 9;28:100899. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2019.100899. eCollection 2019. Respir Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31341763 Free PMC article.
-
Real-life effectiveness of mepolizumab in patients with severe refractory eosinophilic asthma and multiple comorbidities.World Allergy Organ J. 2020 Sep 18;13(9):100462. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100462. eCollection 2020 Sep. World Allergy Organ J. 2020. PMID: 32994855 Free PMC article.
-
The pharmacological management of asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap syndrome (ACOS).Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Feb;21(2):213-231. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1701656. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31955671 Review.
-
Real-world Effectiveness of Mepolizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Ther. 2021 Jun;43(6):e192-e208. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.03.023. Epub 2021 May 4. Clin Ther. 2021. PMID: 33962763
Cited by
-
Exercise Recommendations and Practical Considerations for Asthma Management-An EAACI Position Paper.Allergy. 2025 Jun;80(6):1572-1591. doi: 10.1111/all.16573. Epub 2025 May 6. Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40327018 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of benralizumab on lung volume changes during exercise in experimental setting in severe asthmatics: a pilot study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 23;16:1611168. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1611168. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40771920 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
