High RIPK3 expression is associated with a higher risk of early kidney transplant failure
- PMID: 37868627
- PMCID: PMC10585402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107879
High RIPK3 expression is associated with a higher risk of early kidney transplant failure
Abstract
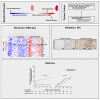
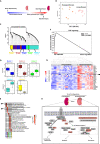
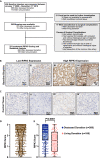
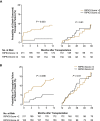
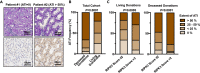
Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is associated with reduced allograft survival, and each additional hour of cold ischemia time increases the risk of graft failure and mortality following renal transplantation. Receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) is a key effector of necroptosis, a regulated form of cell death. Here, we evaluate the first-in-human RIPK3 expression dataset following IRI in kidney transplantation. The primary analysis included 374 baseline biopsy samples obtained from renal allografts 10 minutes after onset of reperfusion. RIPK3 was primarily detected in proximal tubular cells and distal tubular cells, both of which are affected by IRI. Time-to-event analysis revealed that high RIPK3 expression is associated with a significantly higher risk of one-year transplant failure and prognostic for one-year (death-censored) transplant failure independent of donor and recipient associated risk factors in multivariable analyses. The RIPK3 score also correlated with deceased donation, cold ischemia time and the extent of tubular injury.
Keywords: Molecular biology; Nephrology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No author declares a conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hart A., Lentine K.L., Smith J.M., Miller J.M., Skeans M.A., Prentice M., Robinson A., Foutz J., Booker S.E., Israni A.K., et al. OPTN/SRTR 2019 Annual Data Report: Kidney. Am. J. Transplant. 2021;21(Suppl 2):21–137. - PubMed
-
- Tullius S.G., Rabb H. Improving the Supply and Quality of Deceased-Donor Organs for Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;378:1920–1929. - PubMed
-
- Querard A.H., Le Borgne F., Dion A., Giral M., Mourad G., Garrigue V., Rostaing L., Kamar N., Loupy A., Legendre C., et al. Propensity score-based comparison of the graft failure risk between kidney transplant recipients of standard and expanded criteria donor grafts: Toward increasing the pool of marginal donors. Am. J. Transplant. 2018;18:1151–1157. - PubMed
-
- Gill J., Dong J., Rose C., Gill J.S. The risk of allograft failure and the survival benefit of kidney transplantation are complicated by delayed graft function. Kidney Int. 2016;89:1331–1336. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

