Keratoconus Detection-based on Dynamic Corneal Deformation Videos Using Deep Learning
- PMID: 37868800
- PMCID: PMC10587634
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xops.2023.100380
Keratoconus Detection-based on Dynamic Corneal Deformation Videos Using Deep Learning
Abstract
Objective: To assess the performance of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for automated detection of keratoconus (KC) in standalone Scheimpflug-based dynamic corneal deformation videos.
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Participants: We retrospectively analyzed datasets with records of 734 nonconsecutive, refractive surgery candidates, and patients with unilateral or bilateral KC.
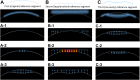
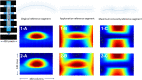
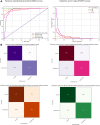
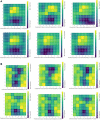
Methods: We first developed a video preprocessing pipeline to translate dynamic corneal deformation videos into 3-dimensional pseudoimage representations and then trained a CNN to directly identify KC from pseudoimages. We calculated the model's KC probability score cut-off and evaluated the performance by subjective and objective accuracy metrics using 2 independent datasets.
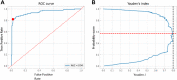
Main outcome measures: Area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC), accuracy, specificity, sensitivity, and KC probability score.
Results: The model accuracy on the test subset was 0.89 with AUC of 0.94. Based on the external validation dataset, the AUC and accuracy of the CNN model for detecting KC were 0.93 and 0.88, respectively.
Conclusions: Our deep learning-based approach was highly sensitive and specific in separating normal from keratoconic eyes using dynamic corneal deformation videos at levels that may prove useful in clinical practice.
Financial disclosures: Proprietary or commercial disclosure may be found in the Footnotes and Disclosures at the end of this article.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Convolutional neural network; Deep learning; Keratoconus; Scheimpflug-based dynamic corneal deformation videos.
© 2023 by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Hybrid Transformers-based Convolutional Neural Network Model for Keratoconus Detection in Scheimpflug-based Dynamic Corneal Deformation Videos.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2025 Jun 18;20:10.18502/jovr.v20.17716. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v20.17716. eCollection 2025. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2025. PMID: 40689120 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a scheimpflug-based biomechanical analyser and tomography in the early detection of subclinical keratoconus in chinese patients.BMC Ophthalmol. 2021 Sep 20;21(1):339. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02102-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34544392 Free PMC article.
-
Localized Corneal Biomechanical Alteration Detected In Early Keratoconus Based on Corneal Deformation Using Artificial Intelligence.Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2023 Nov-Dec 01;12(6):574-581. doi: 10.1097/APO.0000000000000644. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2023. PMID: 37973045
-
Artificial Intelligence-Based Diagnostic Model for Detecting Keratoconus Using Videos of Corneal Force Deformation.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Sep 1;11(9):32. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.9.32. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36178782 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting dry eye from ocular surface videos based on deep learning.Ocul Surf. 2023 Apr;28:90-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2023.01.005. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Ocul Surf. 2023. PMID: 36708879
Cited by
-
Screening with the Bilateral Corneal Symmetry 3-D Analyzer.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 May 9;22(5):747. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22050747. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40427862 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based keratoconus detection from Scheimpflug images.Biomed Opt Express. 2025 Jul 7;16(8):3047-3060. doi: 10.1364/BOE.559663. eCollection 2025 Aug 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2025. PMID: 40809975 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence derived grading of mustard gas induced corneal injury and opacity.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20359. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08042-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594758 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in machine learning for keratoconus diagnosis.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar 30;45(1):128. doi: 10.1007/s10792-025-03496-4. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40159519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and management of keratoconus: a systematic review.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024 May 17;4:1380701. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2024.1380701. eCollection 2024. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38984114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Labiris G., Giarmoukakis A., Sideroudi H., et al. Impact of keratoconus, cross-linking, and cross-linking combined with photorefractive keratectomy on self-reported quality of life. Cornea. 2012;31:734–739. - PubMed
-
- Rabinowitz Y.S. Keratoconus. Surv Ophthalmol. 1998;42:297–319. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosio R., Jr., Belin M.W. Imaging of the cornea: topography vs tomography. J Refract Surg. 2010;26:847–849. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

