Unraveling the relationship between the renin-angiotensin system and endometrial cancer: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 37869088
- PMCID: PMC10585148
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1235418
Unraveling the relationship between the renin-angiotensin system and endometrial cancer: a comprehensive review
Abstract
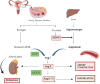
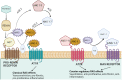
Endometrial cancer (EC), the most common adenocarcinoma, represents 90% of uterine cancer in women with an increased incidence of occurrence attributed to age, obesity, hypertension, and hypoestrogenism. Being the most common gynecological malignancy in women, it shows a relation with the activation of different components of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which is predominantly involved in maintaining blood pressure, salt, water, and aldosterone secretion, thereby playing a significant role in the etiology of hypertension. The components of the RAS, i.e., ACE-I, ACE-II, AT1R, AT2R, and Pro(renin) receptor, are widely expressed in both glandular and stromal cells of the endometrium, with varying levels throughout the different phases of the menstrual cycle. This causes the endometrial RAS to implicate angiogenesis, neovascularization, and cell proliferation. Thus, dysfunctioning of the endometrial RAS could predispose the growth and spread of EC. Interestingly, the increased expression of AngII, AGTR1, and AGTR2 showed advancement in the stages and progression of EC via the prorenin/ATP6AP2 and AngII/AGTR1 pathway. Therefore, this review corresponds to unraveling the relationship between the progression and development of endometrial cancer with the dysfunction in the expression of various components associated with RAS in maintaining blood pressure.
Keywords: ACE; RAS pathway; angiotensin I-II; endometrial cancer; immunosuppressor.
Copyright © 2023 Khan, Elsori, Rashid, Tamanna, Chakraborty, Farooqi, Kar, Sambyal and Kamal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Wik E, Ræder MB, Krakstad C, Trovik J, Birkeland E, Hoivik EA, et al. . Lack of estrogen receptor-α Is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and PI3K alterations in endometrial carcinomaLow ER-α Associates with EMT and PI3K alterations in endometrial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res (2013) 19(5):1094–105. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3039 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Passarello K, Kurian S, Villanueva V. “Endometrial cancer: an overview of pathophysiology, management, and care” in Seminars in oncology nursing. (2019) (WB Saunders; ) 35(2):157–165. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

