Design and fabrication of customizable microneedles enabled by 3D printing for biomedical applications
- PMID: 37869723
- PMCID: PMC10589728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.09.022
Design and fabrication of customizable microneedles enabled by 3D printing for biomedical applications
Abstract
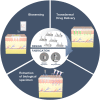
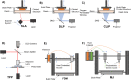
Microneedles (MNs) is an emerging technology that employs needles ranging from 10 to 1000 μm in height, as a minimally invasive technique for various procedures such as therapeutics, disease monitoring and diagnostics. The commonly used method of fabrication, micromolding, has the advantage of scalability, however, micromolding is unable to achieve rapid customizability in dimensions, geometries and architectures, which are the pivotal factors determining the functionality and efficacy of the MNs. 3D printing offers a promising alternative by enabling MN fabrication with high dimensional accuracy required for precise applications, leading to improved performance. Furthermore, enabled by its customizability and one-step process, there is propitious potential for growth for 3D-printed MNs especially in the field of personalized and on-demand medical devices. This review provides an overview of considerations for the key parameters in designing MNs, an introduction on the various 3D-printing techniques for fabricating this new generation of MNs, as well as highlighting the advancements in biomedical applications facilitated by 3D-printed MNs. Lastly, we offer some insights into the future prospects of 3D-printed MNs, specifically its progress towards translation and entry into market.
Keywords: 3D printing; Biosensing; Drug delivery; Extraction of biological specimen; Microneedles.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

