First-Line Selpercatinib or Chemotherapy and Pembrolizumab in RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC
- PMID: 37870973
- PMCID: PMC10698285
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309457
First-Line Selpercatinib or Chemotherapy and Pembrolizumab in RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC
Abstract
Background: Selpercatinib, a highly selective potent and brain-penetrant RET inhibitor, was shown to have efficacy in patients with advanced RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in a nonrandomized phase 1-2 study.
Methods: In a randomized phase 3 trial, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of first-line selpercatinib as compared with control treatment that consisted of platinum-based chemotherapy with or without pembrolizumab at the investigator's discretion. The primary end point was progression-free survival assessed by blinded independent central review in both the intention-to-treat-pembrolizumab population (i.e., patients whose physicians had planned to treat them with pembrolizumab in the event that they were assigned to the control group) and the overall intention-to-treat population. Crossover from the control group to the selpercatinib group was allowed if disease progression as assessed by blinded independent central review occurred during receipt of control treatment.
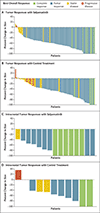
Results: In total, 212 patients underwent randomization in the intention-to-treat-pembrolizumab population. At the time of the preplanned interim efficacy analysis, median progression-free survival was 24.8 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 16.9 to not estimable) with selpercatinib and 11.2 months (95% CI, 8.8 to 16.8) with control treatment (hazard ratio for progression or death, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.31 to 0.70; P<0.001). The percentage of patients with an objective response was 84% (95% CI, 76 to 90) with selpercatinib and 65% (95% CI, 54 to 75) with control treatment. The cause-specific hazard ratio for the time to progression affecting the central nervous system was 0.28 (95% CI, 0.12 to 0.68). Efficacy results in the overall intention-to-treat population (261 patients) were similar to those in the intention-to-treat-pembrolizumab population. The adverse events that occurred with selpercatinib and control treatment were consistent with those previously reported.
Conclusions: Treatment with selpercatinib led to significantly longer progression-free survival than platinum-based chemotherapy with or without pembrolizumab among patients with advanced RET fusion-positive NSCLC. (Funded by Eli Lilly and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04194944.).
Copyright © 2023 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Selpercatinib Shifts Treatment Paradigm for MTC and NSCLC.Cancer Discov. 2023 Dec 12;13(12):OF8. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-ND2023-0011. Cancer Discov. 2023. PMID: 37874126
-
Selpercatinib or Chemotherapy in RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC.N Engl J Med. 2024 Jan 25;390(4):381. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2314327. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 38265653 No abstract available.
-
Selpercatinib or Chemotherapy in RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2024 Jan 25;390(4):381-382. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2314327. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 38265654 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rodríguez-Abreu D, Powell SF, Hochmair MJ, et al. Pemetrexed plus platinum with or without pembrolizumab in patients with previously untreated metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC: protocol-specified final analysis from KEYNOTE-189. Ann Oncol 2021; 32:881–95. - PubMed
-
- Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2022;20: 497–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
