Associations of Biomarkers of Tubular Injury and Inflammation with Biopsy Features in Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 37871959
- PMCID: PMC10843226
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000333
Associations of Biomarkers of Tubular Injury and Inflammation with Biopsy Features in Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Background: Whether biomarkers of tubular injury and inflammation indicate subclinical structural kidney pathology early in type 1 diabetes remains unknown.
Methods: We investigated associations of biomarkers of tubular injury and inflammation with kidney structural features in 244 adults with type 1 diabetes from the Renin-Angiotensin System Study, a randomized, placebo-controlled trial testing effects of enalapril or losartan on changes in glomerular, tubulointerstitial, and vascular parameters from baseline to 5-year kidney biopsies. Biosamples at biopsy were assessed for kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1), soluble TNF receptor 1 (sTNFR1), arginine-to-citrulline ratio in plasma, and uromodulin and epidermal growth factor (EGF) in urine. We examined cross-sectional correlations between biomarkers and biopsy features and baseline biomarker associations with 5-year changes in biopsy features.
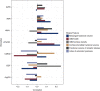
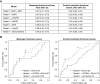
Results: Participants' mean age was 30 years (SD 10) and diabetes duration 11 years (SD 5); 53% were women. The mean GFR measured by iohexol disappearance was 128 ml/min per 1.73 m 2 (SD 19) and median urinary albumin excretion was 5 μ g/min (interquartile range, 3-8). KIM-1 was associated with most biopsy features: higher mesangial fractional volume (0.5% [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.1 to 0.9] greater per SD KIM-1), glomerular basement membrane (GBM) width (14.2 nm [95% CI, 6.5 to 22.0] thicker), cortical interstitial fractional volume (1.1% [95% CI, 0.6 to 1.6] greater), fractional volume of cortical atrophic tubules (0.6% [95% CI, 0.2 to 0.9] greater), and arteriolar hyalinosis index (0.03 [95% CI, 0.1 to 0.05] higher). sTNFR1 was associated with higher mesangial fractional volume (0.9% [95% CI, 0.5 to 1.3] greater) and GBM width (12.5 nm [95% CI, 4.5 to 20.5] thicker) and lower GBM surface density (0.003 μ m 2 / μ m 3 [95% CI, 0.005 to 0.001] lesser). EGF and arginine-to-citrulline ratio correlated with severity of glomerular and tubulointerstitial features. Baseline sTNFR1, uromodulin, and EGF concentrations were associated with 5-year glomerular and tubulointerstitial feature progression.
Conclusions: Biomarkers of tubular injury and inflammation were associated with kidney structural parameters in early type 1 diabetes and may be indicators of kidney disease risk.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: Renin Angiotensin System Study (RASS/B-RASS), NCT00143949.
Podcast: This article contains a podcast at https://dts.podtrac.com/redirect.mp3/www.asn-online.org/media/podcast/CJASN/2023_11_17_CJN0000000000000333.mp3.
Copyright © 2023 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
I.H. de Boer reports consultancy for Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Boehringer-Ingelheim/Lilly, Cyclerion Therapeutics, George Clinical, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Ironwood, Lilly, Medscape, and Otsuka; research funding from DexCom and Novo Nordisk; research equipment and supplies from DexCom; honoraria from National Institutes of Health; and advisory or leadership roles as a Deputy Editor of
Figures

References
-
- de Boer IH Rue TC Cleary PA, et al. . Long-term renal outcomes of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: an analysis of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications cohort. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(5):412–420. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2011.16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01DK125084/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG-024824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK101108/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK129318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG024824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK132399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK132399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4-DK-101108/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK035816/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125084/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK007467/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK035816/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK129318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007467/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

