Feasibility of GPT-3 and GPT-4 for in-Depth Patient Education Prior to Interventional Radiological Procedures: A Comparative Analysis
- PMID: 37872295
- PMCID: PMC10844465
- DOI: 10.1007/s00270-023-03563-2
Feasibility of GPT-3 and GPT-4 for in-Depth Patient Education Prior to Interventional Radiological Procedures: A Comparative Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: This study explores the utility of the large language models, GPT-3 and GPT-4, for in-depth patient education prior to interventional radiology procedures. Further, differences in answer accuracy between the models were assessed.
Materials and methods: A total of 133 questions related to three specific interventional radiology procedures (Port implantation, PTA and TACE) covering general information as well as preparation details, risks and complications and post procedural aftercare were compiled. Responses of GPT-3 and GPT-4 were assessed for their accuracy by two board-certified radiologists using a 5-point Likert scale. The performance difference between GPT-3 and GPT-4 was analyzed.
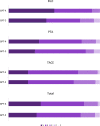
Results: Both GPT-3 and GPT-4 responded with (5) "completely correct" (4) "very good" answers for the majority of questions ((5) 30.8% + (4) 48.1% for GPT-3 and (5) 35.3% + (4) 47.4% for GPT-4). GPT-3 and GPT-4 provided (3) "acceptable" responses 15.8% and 15.0% of the time, respectively. GPT-3 provided (2) "mostly incorrect" responses in 5.3% of instances, while GPT-4 had a lower rate of such occurrences, at just 2.3%. No response was identified as potentially harmful. GPT-4 was found to give significantly more accurate responses than GPT-3 (p = 0.043).
Conclusion: GPT-3 and GPT-4 emerge as relatively safe and accurate tools for patient education in interventional radiology. GPT-4 showed a slightly better performance. The feasibility and accuracy of these models suggest their promising role in revolutionizing patient care. Still, users need to be aware of possible limitations.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Chat-GPT; Interventional radiology; Large language models; Patient education.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
From Search Engines to Large Language Models: A Big Leap for Patient Education!Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024 Feb;47(2):251-252. doi: 10.1007/s00270-024-03658-4. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38263526 No abstract available.
References
-
- Athaluri SA, Manthena SV, Kesapragada VSRKM, Yarlagadda V, Dave T, Duddumpudi RTS. Exploring the boundaries of reality: investigating the phenomenon of artificial intelligence hallucination in scientific writing through ChatGPT REferences. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37432. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37432. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous