This is a preprint.
Perceptual formant discrimination during speech movement planning
- PMID: 37873157
- PMCID: PMC10592784
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.10.11.561423
Perceptual formant discrimination during speech movement planning
Update in
-
Perceptual formant discrimination during speech movement planning.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 2;19(4):e0301514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301514. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38564597 Free PMC article.
Abstract
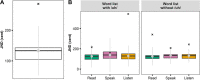
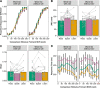
Evoked potential studies have shown that speech planning modulates auditory cortical responses. The phenomenon's functional relevance is unknown. We tested whether, during this time window of cortical auditory modulation, there is an effect on speakers' perceptual sensitivity for vowel formant discrimination. Participants made same/different judgments for pairs of stimuli consisting of a pre-recorded, self-produced vowel and a formant-shifted version of the same production. Stimuli were presented prior to a "go" signal for speaking, prior to passive listening, and during silent reading. The formant discrimination stimulus /uh/ was tested with a congruent productions list (words with /uh/) and an incongruent productions list (words without /uh/). Logistic curves were fitted to participants' responses, and the just-noticeable difference (JND) served as a measure of discrimination sensitivity. We found a statistically significant effect of condition (worst discrimination before speaking) without congruency effect. Post-hoc pairwise comparisons revealed that JND was significantly greater before speaking than during silent reading. Thus, formant discrimination sensitivity was reduced during speech planning regardless of the congruence between discrimination stimulus and predicted acoustic consequences of the planned speech movements. This finding may inform ongoing efforts to determine the functional relevance of the previously reported modulation of auditory processing during speech planning.
Keywords: auditory feedback; formant discrimination; sensory gating; sensory modulation; sensory prediction; speech production.
Figures

References
-
- Bäß P., Jacobsen T., & Schröger E. (2008). Suppression of the auditory N1 event-related potential component with unpredictable self-initiated tones: Evidence for internal forward models with dynamic stimulation. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 70(2), 137–143. 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2008.06.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Behroozmand R., Karvelis L., Liu H., & Larson C. R. (2009). Vocalization-induced enhancement of the auditory cortex responsiveness during voice F0 feedback perturbation. Clinical Neurophysiology: Official Journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology, 120(7), 1303–1312. 10.1016/J.CLINPH.2009.04.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
