This is a preprint.
Multidimensional Analysis of the Adult Human Heart in Health and Disease using Hierarchical Phase-Contrast Tomography (HiP-CT)
- PMID: 37873359
- PMCID: PMC10592740
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.10.09.561474
Multidimensional Analysis of the Adult Human Heart in Health and Disease using Hierarchical Phase-Contrast Tomography (HiP-CT)
Update in
-
Multidimensional Analysis of the Adult Human Heart in Health and Disease Using Hierarchical Phase-Contrast Tomography.Radiology. 2024 Jul;312(1):e232731. doi: 10.1148/radiol.232731. Radiology. 2024. PMID: 39012246 Free PMC article.
Abstract
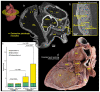
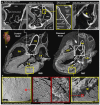
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a leading cause of death worldwide. Current clinical imaging modalities provide resolution adequate for diagnosis but are unable to provide detail of structural changes in the heart, across length-scales, necessary for understanding underlying pathophysiology of disease. Hierarchical Phase-Contrast Tomography (HiP-CT), using new (4th) generation synchrotron sources, potentially overcomes this limitation, allowing micron resolution imaging of intact adult organs with unprecedented detail. In this proof of principle study (n=2), we show the utility of HiP-CT to image whole adult human hearts ex-vivo: one 'control' without known cardiac disease and one with multiple known cardiopulmonary pathologies. The resulting multiscale imaging was able to demonstrate exemplars of anatomy in each cardiac segment along with novel findings in the cardiac conduction system, from gross (20 um/voxel) to cellular scale (2.2 um/voxel), non-destructively, thereby bridging the gap between macroscopic and microscopic investigations. We propose that the technique represents a significant step in virtual autopsy methods for studying structural heart disease, facilitating research into abnormalities across scales and age-groups. It opens up possibilities for understanding and treating disease; and provides a cardiac 'blueprint' with potential for in-silico simulation, device design, virtual surgical training, and bioengineered heart in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Wilkins E, Wilson L, Wickramasinghe K, Bhatnagar P, Leal J, Luengo-Fernandez R, et al. European cardiovascular disease statistics 2017. Eur Heart Netw. 2017;
-
- Haugaa KH, Aabel EW. Mitral Annular Disjunction: Normal or Abnormal. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022. Nov;15(11):1867–9. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
