This is a preprint.
STING induces HOIP-mediated synthesis of M1 ubiquitin chains to stimulate NFκB signaling
- PMID: 37873486
- PMCID: PMC10592814
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.10.14.562349
STING induces HOIP-mediated synthesis of M1 ubiquitin chains to stimulate NFκB signaling
Update in
-
STING induces HOIP-mediated synthesis of M1 ubiquitin chains to stimulate NF-κB signaling.EMBO J. 2025 Jan;44(1):141-165. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00291-2. Epub 2024 Nov 22. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 39578541 Free PMC article.
Abstract
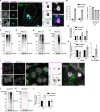
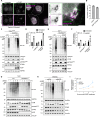
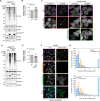
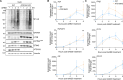
STING activation by cyclic dinucleotides in mammals induces IRF3- and NFκB -mediated gene expression, and the lipidation of LC3B at Golgi-related membranes. While mechanisms of the IRF3 response are well understood, the mechanisms of NFκB activation mediated by STING remain unclear. We report that STING activation induces linear/M1-linked ubiquitin chain (M1-Ub) formation and recruitment of the LUBAC E3 ligase, HOIP, to LC3B-associated Golgi membranes where ubiquitin is also localized. Loss of HOIP prevents formation of M1-Ub ubiquitin chains and reduces STING-induced NFκB and IRF3-mediated signaling in human monocytic THP1 cells and mouse bone marrow derived macrophages, without affecting STING activation. STING-induced LC3B lipidation is not required for M1-Ub chain formation or the immune-related gene expression, however the recently reported function of STING to neutralize the pH of the Golgi may be involved. Thus, LUBAC synthesis of M1 ubiquitin chains mediates STING-induced innate immune signaling.
Keywords: Golgi; Innate Immunity; Interferon; LC3B; LUBAC.
Figures





References
-
- Ablasser A & Chen ZJ (2019) cGAS in action: Expanding roles in immunity and inflammation. Science 363: eaat8657. - PubMed
-
- Balka KR, Louis C, Saunders TL, Smith AM, Calleja DJ, D’Silva DB, Moghaddas F, Tailler M, Lawlor KE, Zhan Y, et al. (2020) TBK1 and IKKε Act Redundantly to Mediate STING-Induced NF-κB Responses in Myeloid Cells. Cell Reports 31 - PubMed
-
- Blasi E, Radzioch D, Durum SK & Varesio L (1987) A murine macrophage cell line, immortalized by v-raf and v-myc oncogenes, exhibits normal macrophage functions. Eur J Immunol 17: 1491–1498 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
