Identification of Plasma Biomarkers from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Using an Optimized Sequential Window Acquisition of All THeoretical Mass Spectra (SWATH) Proteomics Workflow
- PMID: 37873874
- PMCID: PMC10594463
- DOI: 10.3390/proteomes11040032
Identification of Plasma Biomarkers from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Using an Optimized Sequential Window Acquisition of All THeoretical Mass Spectra (SWATH) Proteomics Workflow
Abstract
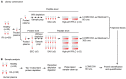
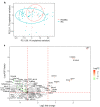
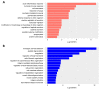
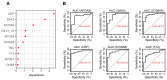
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Plasma biomarkers are critical for understanding disease mechanisms, treatment effects, and diagnosis. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics is a powerful tool for unbiased biomarker discovery. However, plasma proteomics is significantly hampered by signal interference from high-abundance proteins, low overall protein coverage, and high levels of missing data from data-dependent acquisition (DDA). To achieve quantitative proteomics analysis for plasma samples with a balance of throughput, performance, and cost, we developed a workflow incorporating plate-based high abundance protein depletion and sample preparation, comprehensive peptide spectral library building, and data-independent acquisition (DIA) SWATH mass spectrometry-based methodology. In this study, we analyzed plasma samples from both RA patients and healthy donors. The results showed that the new workflow performance exceeded that of the current state-of-the-art depletion-based plasma proteomic platforms in terms of both data quality and proteome coverage. Proteins from biological processes related to the activation of systemic inflammation, suppression of platelet function, and loss of muscle mass were enriched and differentially expressed in RA. Some plasma proteins, particularly acute-phase reactant proteins, showed great power to distinguish between RA patients and healthy donors. Moreover, protein isoforms in the plasma were also analyzed, providing even deeper proteome coverage. This workflow can serve as a basis for further application in discovering plasma biomarkers of other diseases.
Keywords: DIA; SWATH; biomarker; plasma; protein isoform; proteomics; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
AbbVie funded the study and participated in study design, research, data collection, analysis and interpretation of data, writing, reviewing, and approving the publication. There are no additional conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization of Acquisition and Data-Processing Parameters for Improved Proteomic Quantification by Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectrometry.J Proteome Res. 2017 Feb 3;16(2):738-747. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00767. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Proteome Res. 2017. PMID: 27995803
-
High throughput and accurate serum proteome profiling by integrated sample preparation technology and single-run data independent mass spectrometry analysis.J Proteomics. 2018 Mar 1;174:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.12.014. Epub 2017 Dec 24. J Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29278786
-
Use of a Recombinant Biomarker Protein DDA Library Increases DIA Coverage of Low Abundance Plasma Proteins.J Proteome Res. 2021 May 7;20(5):2374-2389. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00898. Epub 2021 Mar 22. J Proteome Res. 2021. PMID: 33752330
-
Advances in data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry towards comprehensive digital proteome landscape.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023 Nov-Dec;42(6):2324-2348. doi: 10.1002/mas.21781. Epub 2022 May 29. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2023. PMID: 35645145 Review.
-
Clinical veterinary proteomics: Techniques and approaches to decipher the animal plasma proteome.Vet J. 2017 Dec;230:6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2017.10.022. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Vet J. 2017. PMID: 29208216 Review.
Cited by
-
Alpha-Taxilin: A Potential Diagnosis and Therapeutics Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis Which Interacts with Key Glycolytic Enzymes Associated with Metabolic Shifts in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Nov 29;17:10027-10045. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S465051. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39634288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salman E., Çetiner S., Boral B., Kibar F., Erken E., Ersözlü E.D., Badak S.Ö., Salman R.B., Sertdemir Y., Duran A.Ç., et al. Importance of 14-3-3eta, Anti-CarP, and Anti-Sa in the Diagnosis of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis. Turk. J. Méd. Sci. 2019;49:1498–1502. doi: 10.3906/sag-1812-137. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tenstad H.B., Nilsson A.C., Dellgren C.D., Lindegaard H.M., Rubin K.H., Lillevang S.T. Use and Utility of Serologic Tests for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Primary Care. Dan. Méd. J. 2020;67:A05190318b. - PubMed
-
- Assarsson E., Lundberg M., Holmquist G., Björkesten J., Thorsen S.B., Ekman D., Eriksson A., Dickens E.R., Ohlsson S., Edfeldt G., et al. Homogenous 96-Plex PEA Immunoassay Exhibiting High Sensitivity, Specificity, and Excellent Scalability. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e95192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095192. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

