Methylprednisolone therapy induces differential metabolic trajectories in severe COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 37874139
- PMCID: PMC10734516
- DOI: 10.1128/msystems.00726-23
Methylprednisolone therapy induces differential metabolic trajectories in severe COVID-19 patients
Abstract
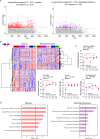
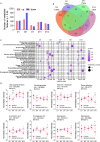
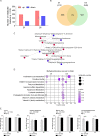
The SARS-CoV-2 virus infection in humans induces significant inflammatory and systemic reactions and complications of which corticosteroids like methylprednisolone have been recommended as treatment. Our understanding of the metabolic and metabolomic pathway dysregulations while using intravenous corticosteroids in COVID-19 is limited. This study will help enlighten the metabolic and metabolomic pathway dysregulations underlying high daily doses of intravenous methylprednisolone in COVID-19 patients compared to those receiving placebo. The information on key metabolites and pathways identified in this study together with the crosstalk with the inflammation and biochemistry components may be used, in the future, to leverage the use of methylprednisolone in any future pandemics from the coronavirus family.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 virus; corticosteroid; metabolomics; methylprednisolone; profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jeronimo CMP, Farias MEL, Val FFA, Sampaio VS, Alexandre MAA, Melo GC, Safe IP, Borba MGS, Netto RLA, Maciel ABS, Neto JRS, Oliveira LB, Figueiredo EFG, Oliveira Dinelly KM, de Almeida Rodrigues MG, Brito M, Mourão MPG, Pivoto João GA, Hajjar LA, Bassat Q, Romero GAS, Naveca FG, Vasconcelos HL, de Araújo Tavares M, Brito-Sousa JD, Costa FTM, Nogueira ML, Baía-da-Silva DC, Xavier MS, Monteiro WM, Lacerda MVG, MetCOVID Team . 2021. Methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for patients hospitalized with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19; MetCOVID): a randomized, double-blind, phase IIb, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis 72:e373–e381. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1177 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, Mafham M, Bell JL, Linsell L, Staplin N, Brightling C, Ustianowski A, Elmahi E, Prudon B, Green C, Felton T, Chadwick D, Rege K, Fegan C, Chappell LC, Faust SN, Jaki T, Jeffery K, Montgomery A, Rowan K, Juszczak E, Baillie JK, Haynes R, Landray MJ, RECOVERY Collaborative Group . 2021. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. N Engl J Med 384:693–704. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

