Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound (Tongxinluo) and Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction: The CTS-AMI Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37874574
- PMCID: PMC10599127
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.19524
Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound (Tongxinluo) and Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction: The CTS-AMI Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Tongxinluo, a traditional Chinese medicine compound, has shown promise in in vitro, animal, and small human studies for myocardial infarction, but has not been rigorously evaluated in large randomized clinical trials.
Objective: To investigate whether Tongxinluo could improve clinical outcomes in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
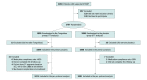
Design, setting, and participants: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted among patients with STEMI within 24 hours of symptom onset from 124 hospitals in China. Patients were enrolled from May 2019 to December 2020; the last date of follow-up was December 15, 2021.
Interventions: Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either Tongxinluo or placebo orally for 12 months (a loading dose of 2.08 g after randomization, followed by the maintenance dose of 1.04 g, 3 times a day), in addition to STEMI guideline-directed treatments.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was 30-day major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCEs), a composite of cardiac death, myocardial reinfarction, emergent coronary revascularization, and stroke. Follow-up for MACCEs occurred every 3 months to 1 year.
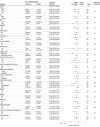
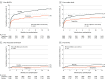
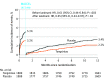
Results: Among 3797 patients who were randomized, 3777 (Tongxinluo: 1889 and placebo: 1888; mean age, 61 years; 76.9% male) were included in the primary analysis. Thirty-day MACCEs occurred in 64 patients (3.4%) in the Tongxinluo group vs 99 patients (5.2%) in the control group (relative risk [RR], 0.64 [95% CI, 0.47 to 0.88]; risk difference [RD], -1.8% [95% CI, -3.2% to -0.6%]). Individual components of 30-day MACCEs, including cardiac death (56 [3.0%] vs 80 [4.2%]; RR, 0.70 [95% CI, 0.50 to 0.99]; RD, -1.2% [95% CI, -2.5% to -0.1%]), were also significantly lower in the Tongxinluo group than the placebo group. By 1 year, the Tongxinluo group continued to have lower rates of MACCEs (100 [5.3%] vs 157 [8.3%]; HR, 0.64 [95% CI, 0.49 to 0.82]; RD, -3.0% [95% CI, -4.6% to -1.4%]) and cardiac death (85 [4.5%] vs 116 [6.1%]; HR, 0.73 [95% CI, 0.55 to 0.97]; RD, -1.6% [95% CI, -3.1% to -0.2%]). There were no significant differences in other secondary end points including 30-day stroke; major bleeding at 30 days and 1 year; 1-year all-cause mortality; and in-stent thrombosis (<24 hours; 1-30 days; 1-12 months). More adverse drug reactions occurred in the Tongxinluo group than the placebo group (40 [2.1%] vs 21 [1.1%]; P = .02), mainly driven by gastrointestinal symptoms.
Conclusions and relevance: In patients with STEMI, the Chinese patent medicine Tongxinluo, as an adjunctive therapy in addition to STEMI guideline-directed treatments, significantly improved both 30-day and 1-year clinical outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the mechanism of action of Tongxinluo in STEMI.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03792035.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Meets Evidence-Based Medicine in the Acutely Infarcted Heart.JAMA. 2023 Oct 24;330(16):1529-1530. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.20838. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37874582 No abstract available.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound and Clinical Outcomes in Acute Myocardial Infarction.JAMA. 2024 Apr 16;331(15):1332. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.0620. JAMA. 2024. PMID: 38506843 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hillerson D, Li S, Misumida N, et al. . Characteristics, process metrics, and outcomes among patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction in rural vs urban areas in the US: a report from the US National Cardiovascular Data Registry. JAMA Cardiol. 2022;7(10):1016-1024. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2022.2774 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

