LRRK2 G2019S promotes astrocytic inflammation induced by oligomeric α-synuclein through NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 37876795
- PMCID: PMC10590863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108130
LRRK2 G2019S promotes astrocytic inflammation induced by oligomeric α-synuclein through NF-κB pathway
Abstract
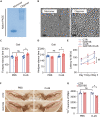
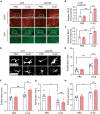
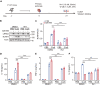
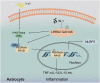
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by the irreversible loss of dopaminergic neurons and the accumulation of α-synuclein in Lewy bodies. The oligomeric α-synuclein (O-αS) is the most toxic form of α-synuclein species, and it has been reported to be a robust inflammatory mediator. Mutations in Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (LRRK2) are also genetically linked to PD and neuroinflammation. However, how O-αS and LRRK2 interact in glial cells remains unclear. Here, we reported that LRRK2 G2019S mutation, which is one of the most frequent causes of familial PD, enhanced the effects of O-αS on astrocytes both in vivo and in vitro. Meanwhile, inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity could relieve the inflammatory effects of both LRRK2 G2019S and O-αS. We also demonstrated that nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway might be involved in the neuroinflammatory responses. These findings revealed that inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity may be a viable strategy for suppressing neuroinflammation in PD.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Immunology; Molecular biology; Neuroscience.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Majbour N.K., Abdi I.Y., Dakna M., Wicke T., Lang E., Ali Moussa H.Y., Thomas M.A., Trenkwalder C., Safieh-Garabedian B., Tokuda T., et al. Cerebrospinal alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Reflect Disease Motor Severity in DeNoPa Longitudinal Cohort. Mov. Disord. 2021;36:2048–2056. doi: 10.1002/mds.28611. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

