WIP1 is a novel specific target for growth hormone action
- PMID: 37876819
- PMCID: PMC10590974
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108117
WIP1 is a novel specific target for growth hormone action
Abstract
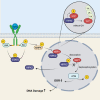
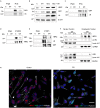
DNA damage repair (DDR) is mediated by phosphorylating effectors ATM kinase, CHK2, p53, and γH2AX. We showed earlier that GH suppresses DDR by suppressing pATM, resulting in DNA damage accumulation. Here, we show GH acting through GH receptor (GHR) inducing wild-type p53-inducible phosphatase 1 (WIP1), which dephosphorylated ATM and its effectors in normal human colon cells and three-dimensional human intestinal organoids. Mice bearing GH-secreting xenografts exhibited induced colon WIP1 with suppressed pATM and γH2AX. WIP1 was also induced in buffy coats derived from patients with elevated GH from somatotroph adenomas. In contrast, decreased colon WIP1 was observed in GHR-/- mice. WIP1 inhibition restored ATM phosphorylation and reversed GH-induced DNA damage. We elucidated a novel GH signaling pathway activating Src/AMPK to trigger HIPK2 nuclear-cytoplasmic relocation and suppressing WIP1 ubiquitination. Concordantly, blocking either AMPK or Src abolished GH-induced WIP1. We identify WIP1 as a specific target for GH-mediated epithelial DNA damage accumulation.
Keywords: biochemistry; molecular biology; physiology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

