Quantum Dot Nanomaterials: Preparation, Characterization, Advanced Bio-Imaging and Therapeutic Applications
- PMID: 37878236
- PMCID: PMC11604693
- DOI: 10.1007/s10895-023-03472-0
Quantum Dot Nanomaterials: Preparation, Characterization, Advanced Bio-Imaging and Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
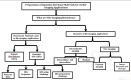
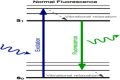
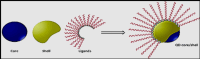
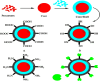
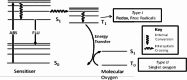
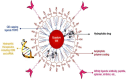
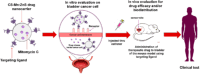
The bio-imaging technology is one of the most significant modern applications used in several fields, including early diagnosis of many illnesses that are most important diseases facing humanity and other vital uses. The primary advancement in nanotechnology is the creation of innovative fluorescence probes called quantum dots (QDs). The use of molecular tagging in research, in vivo, and in vitro studies is revolutionized by quantum dots. The application of QD indicates conversion in natural imaging and photography has demonstrated extraordinary appropriateness in bio-imaging, the discovery of novel drugs, and delivery of targeted genes, biosensing, photodynamic therapy, and diagnosis. New potential methods of early cancer detection and treatment management are being researched as a result of the special physical and chemical characteristics of QD probes. The bio-imaging technique depends on the fluorescent emission of the used materials, which is paired with living cells that are easy to see it in 3D without any surgical intervention. Therefore, the use of QDs many types that have unique and appropriate properties for use in that application; In terms of fluorescent emission strength, duration and luminosity.This review article displays some methods of preparation for QDs nanomaterials and the devices used in this. In addition, it presentssome of challenges that must be avoided for the possibility of using them in the bio-imaging field; as toxicity, bio-compatibility, and hydrophilization. It's reviewed some of the devices that use QDs in bio-imaging technique, the QDs application in cell analysis-imaging, and QDs application in vivo imaging.
Keywords: Bio-imaging; Fluorescence Emission; Quantum dot Applications; Quantum dot Techniques; Vivo Imaging.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical Approval: Not required for this review manuscript since it does not involve any biological experiments. Consent to Participate: Authors have their consent to participate in the paper. Consent for Publication: All authors gave their consent to publish this review article in the present form. Conflict of Interest: All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: properties, applications andtoxicities.Arab J Chem12: 908-931. 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
-
- Rempel SV, Razvodov AA, Nebogatikov MS, Shishkina EV, Shurb VYa, Rempel AA (2013) Sizes and fluorescence of cadmium sulfide quantum dots. Phys Solid State 55:624–628. 10.1134/S1063783413030244
-
- Wegner KD, Hildebrandt N (2015) Quantum dots: bright and versatile in vitro andin vivo fluorescence imaging biosensors. Chem Soc Rev 44:4792–4834. 10.1039/C4CS00532E - PubMed
-
- Wu FG, Zhang X, Kai X, Zhang M, Wang HY, Myers JN, Weng Y, Liu P, Gu N, Chen Z (2015) One-step synthesis of superbright water-soluble siliconnanoparticles with photoluminescence quantum yieldexceeding 80%. Adv Mater Interfaces 2:1500360–1500371. 10.1002/admi.201500360
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

