Stent for life initiative in Portugal: Progress through years and Covid-19 impact
- PMID: 37878596
- PMCID: PMC10599499
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284915
Stent for life initiative in Portugal: Progress through years and Covid-19 impact
Abstract
Background: During Stent for Life Initiative in Portugal lifetime, positive changes in ST elevation myocardial infarction treatment were observed, by the increase of Primary Angioplasty numbers and improvements in patients' behaviour towards myocardial infarction, with an increase in those who called 112 and the lower proportion attending non primary percutaneous coronary intervention centres. Despite public awareness campaigns and system educational programmes, patient and system delay did not change significantly over this period. The aim of this study was to address the public awareness campaign effectiveness on peoples' behaviour facing STEMI, and how Covid-19 has affected STEMI treatment.
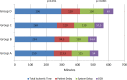
Methods: Data from 1381 STEMI patients were collected during a one-month period each year, from 2011 to 2016, and during one and a half month, matching first lockdown in Portugal 2020. Four groups were constituted: Group A (2011); Group B (2012&2013); Group C (2015&2016) and group D (2020).
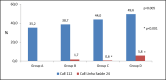
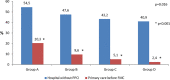
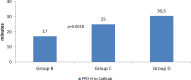
Results: The proportion of patients who called 112, increased significantly (35.2% Group A; 38.7% Group B; 44.0% Group C and 49.6% Group D, p = 0.005); significant reduction was observed in the proportion of patients who attended healthcare centres without PPCI (54.5% group A; 47.6% Group B; 43.2% Group C and 40.9% Group D, p = 0.016), but there were no differences on groups comparison. Total ischemic time, measured from symptoms onset to reperfusion increased progressively from group A [250.0 (178.0-430.0)] to D [296.0 (201.0-457.5.8)] p = 0.012, with statistically significant difference between group C and D (p = 0.034).
Conclusions: During the term of SFL initiative in Portugal, patients resorted less to primary health centres and called more to 112. These results can be attributed the public awareness campaign. Nevertheless, patient and system delays did not significantly change over this period, mainly in late years of SFL, probably for low efficacy of campaigns and in 2020 due to Covid-19 pandemic.
Copyright: © 2023 Pereira et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

