Systematic Mutation and Unnatural Base Pair Incorporation Improves Riboswitch-Based Biosensor Response Time
- PMID: 37878677
- PMCID: PMC10749561
- DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.3c01266
Systematic Mutation and Unnatural Base Pair Incorporation Improves Riboswitch-Based Biosensor Response Time
Abstract
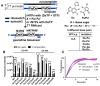
Engineered RNAs have applications in diverse fields from biomedical to environmental. In many cases, the folding of the RNA is critical to its function. Here we describe a strategy to improve the response time of a riboswitch-based fluorescent biosensor. Systematic mutagenesis was performed to either make transpose or transition base pair mutants or introduce orthogonal base pairs. Both natural and unnatural base pair mutants were found to improve the biosensor response time without compromising fold turn-on or ligand affinity. These strategies can be transferred to improve the performance of other RNA-based tools.
Keywords: RNA-based fluorescent biosensors; base pair mutagenesis; guanidine; orthogonal base pairs; rapid sensing; riboswitch folding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Authors MK and IH have financial interests in Xenolis Ptd Ltd.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

