Determining reference ranges for immunological cells of healthy indigenous individuals from a region in Brazil
- PMID: 37878969
- PMCID: PMC10567104
- DOI: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2023AO0291
Determining reference ranges for immunological cells of healthy indigenous individuals from a region in Brazil
Abstract
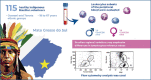
Morais et al. conducted a pioneering study with Brazilian indigenous populations to determine reference values for immunologic cells from healthy adult individuals. The main findings included a higher relative median for T lymphocyte subsets in females than males, and T CD3+, T CD4+, and T CD8+ relative values were statistically different when compared with Brazilian populations from other Brazilian regions. The relative medians of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells were significantly higher in women than in men in a healthy indigenous population. Demographic and ethnic diversity of the Brazilian population can be associated with quantitative modifications in the immunologic cells of healthy individuals.
Objective: The establishment of reference values for a subset of leukocytes is common in clinical practice, and ethnic variations are strongly associated with disease development. In Brazil, indigenous people are vulnerable to infections, and few studies have described the health and disease conditions of this population. This study aimed to provide reference values for immunological cell subsets in indigenous Brazilians living in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul.
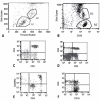
Methods: Flow cytometry and 4-color combinations of monoclonal antibodies were used to characterize cells. A total of 115 healthy adults, mostly females (72%), were included in the study. The results are presented as mean and median (2.5%-97.5% percentiles) for T and B lymphocytes, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, Natural Killer cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells, providing an average immunological profile for the population in question.
Results: The relative medians of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells were significantly higher in women than in men in a healthy indigenous population.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, cell reference data from indigenous Brazilians are unknown in the literature. The immune cell results presented in this pioneering study will contribute to the clinical and laboratory evaluation of the Brazilian indigenous population, especially given the important differences when compared with other Brazilian ethnic groups.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none.
Figures

References
-
- Shakya G, Dumre SP, Malla S, Sharma M, Kc KP, Chhetri DB, et al. Values of lymphocyte subsets in Nepalese healthy adult population. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2012;52(185):6–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

