Quantification of circulating HBV RNA expressed from intrahepatic cccDNA in untreated and NUC treated patients with chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 37879886
- PMCID: PMC10958289
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330644
Quantification of circulating HBV RNA expressed from intrahepatic cccDNA in untreated and NUC treated patients with chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
Objective: A convenient, reproducible biomarker of hepatitis B virus (HBV) covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) transcriptional activity is lacking. We measured circulating HBV RNA (cirB-RNA) in untreated and nucleos(t)ide analogues (NUC) treated chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients to define its correlation with intrahepatic viral markers and HBV core-related antigen (HBcrAg).
Design: Paired liver biopsy and serum samples were collected from 122 untreated and 30 NUC-treated CHB patients. We measured cirB-RNA, HBV DNA, hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), HBcrAg and alanine aminotransferase levels. cirB-RNA was quantified using an investigational HBV RNA assay for use on the cobas 6800 system. The test detects a region spanning the HBV canonical polyadenylation site. cccDNA and 3.5 kb RNA in liver tissue were assessed by quantitative PCR and droplet digital PCR.
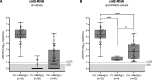
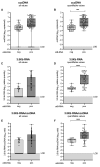
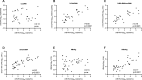
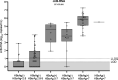
Results: cirB-RNA was detectable in 100% of HBeAg(+) chronic hepatitis (CH), 57% and 14% of HBeAg(-) CH and chronic infection untreated patients and 47% of NUC-treated patients. cirB-RNA undetectability was associated with lower intrahepatic cccDNA transcriptional activity, as well as serum HBcrAg, but no significant differences in HBsAg, in both untreated and treated patients. In untreated HBeAg(-) patients, cirB-RNA correlated with intrahepatic 3.5 kb RNA and cccDNA transcriptional activity, serum HBV DNA and HBcrAg, but not with HBsAg or total cccDNA levels. Combined undetectability of both cirB-RNA and HBcrAg detection in untreated HBeAg(-) patients identified a subgroup with the lowest levels of intrahepatic transcriptionally active cccDNA.
Conclusion: Our results support the usefulness of quantification of circulating HBV RNA expressed from cccDNA as an indicator of intrahepatic active viral reservoir in both untreated and NUC-treated CHB patients.
Trial registration number: NCT02602847.
Keywords: RNA expression; chronic viral hepatitis; hepatitis B; liver biopsy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: BS, AH and MH are employees and stockholders of Roche Molecular Systems (Pleasanton, CA, USA). ED served as speaker for Gilead and Abbvie, participated in advisory board of Gilead, Abbvie and Roche, received grant from Gilead and travel grant from Gilead and Advanz Pharma. PL served as speaker and/or participated in advisory board for Roche Pharma/Diagnostics, Gilead Sciences, GSK, Abbvie, Janssen, Myr, Eiger, Antios, Aligos, Vir, Grifols, Altona, Roboscreen. FZ received consulting fees from: Aligos, Antios, Assembly, Gilead, GSK; FZ and BT received research funding to INSERM from: Assembly, Beam Therapeutics, Blue Jay and Janssen. FZ is an Associate Editor of the journal.
Figures

Comment in
-
Clinical applications of circulating HBV RNA as a potential surrogate biomarker for intrahepatic cccDNA transcriptional activity.Gut. 2024 Mar 7;73(4):563-566. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-331217. Gut. 2024. PMID: 38123992 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Fact sheets, hepatitis B. n.d. Available: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu, European Association for the Study of the Liver . EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2017;67:370–98. 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.021 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
