Patient-centric assessment of rheumatoid arthritis using a smartwatch and bespoke mobile app in a clinical setting
- PMID: 37880288
- PMCID: PMC10600111
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-45387-7
Patient-centric assessment of rheumatoid arthritis using a smartwatch and bespoke mobile app in a clinical setting
Abstract
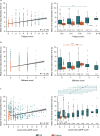
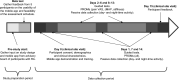
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a fluctuating progressive disease requiring frequent symptom assessment for appropriate management. Continuous tracking using digital technologies may provide greater insights of a patient's experience. This prospective study assessed the feasibility, reliability, and clinical utility of using novel digital technologies to remotely monitor participants with RA. Participants with moderate to severe RA and non-RA controls were monitored continuously for 14 days using an iPhone with an integrated bespoke application and an Apple Watch. Participants completed patient-reported outcome measures and objective guided tests designed to assess disease-related impact on physical function. The study was completed by 28 participants with RA, 28 matched controls, and 2 unmatched controls. Completion rates for all assessments were > 97% and were reproducible over time. Several guided tests distinguished between RA and control cohorts (e.g., mean lie-to-stand time [seconds]: RA: 4.77, control: 3.25; P < 0.001). Participants with RA reporting greater stiffness, pain, and fatigue had worse guided test performances (e.g., wrist movement [P < 0.001] and sit-to-stand transition time [P = 0.009]) compared with those reporting lower stiffness, pain, and fatigue. This study demonstrates that digital technologies can be used in a well-controlled, remote clinical setting to assess the daily impact of RA.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
VH, LGG, AM, WHC, RT, and RW are employees of GSK and own stocks/shares in GSK and Haleon. CL, CWY, PB, JB, JL, MD, MY, and MSD are employees of Analysis Group, which received research funding from GSK to conduct the study. EAM is an employee of Reliant Medical Group, which received research funding from GSK to conduct the study.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

