Skimmianine attenuates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating PI3K-AKT signaling pathway-mediated inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress
- PMID: 37880319
- PMCID: PMC10600244
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-45354-2
Skimmianine attenuates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating PI3K-AKT signaling pathway-mediated inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress
Abstract
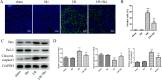
Liver ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is a common injury after liver transplantation and hepatectomy. Skimmianine (Ski) has antibacterial, antiviral pharmacological effects. However, it is not clear whether Ski has a protective effect against liver I/R injury. In the present study, we established a mouse liver I/R model and an AML12 cell hypoxia-reoxygenation (H/R) model, both pretreated with different concentrations of Ski. Serum transaminase levels, necrotic liver area, cell viability, inflammatory factors, oxidative stress and apoptosis-related levels were measured to assess the protective effect of Ski against liver I/R injury. Western blotting was used to detect apoptosis-related proteins and PI3K-AKT pathway-related proteins. Mice and cells were also treated with PI3K inhibitor LY294002 to assess changes in indicators of liver injury. The results showed that Ski significantly reduced transaminase levels, liver necrosis area, oxidative stress, and apoptosis levels in mice with I/R. Ski also inhibited cell injury and apoptosis after H/R. Moreover, Ski activated phosphorylation of PI3K-AKT pathway-related proteins after liver I/R and cell H/R. Importantly, the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 effectively reversed the alleviation of I/R injury caused by Ski. These results confirm that Ski exerts a protective effect against liver I/R injury through activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Pectolinarigenin attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via activation of the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 signaling pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Dec 1;386:110763. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110763. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 37832626
-
Methyl eugenol attenuates liver ischemia reperfusion injury via activating PI3K/Akt signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Oct;99:108023. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108023. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34358859
-
Myricitrin pretreatment ameliorates mouse liver ischemia reperfusion injury.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Dec;89(Pt A):107005. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107005. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33045574
-
Galangin Alleviates Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in a Rat Model by Mediating the PI3K/AKT Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(3):1354-1363. doi: 10.1159/000495553. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30481779
-
Role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver ischemia reperfusion injury: a narrative review.Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Feb;11(2):806-817. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3286. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Ann Palliat Med. 2022. PMID: 35016518 Review.
Cited by
-
Skimmianine Showed Neuroprotection against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 12;46(7):7373-7385. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070437. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057078 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of selected alkaloids on postnatal neurogenesis - in vivo and in vitro studies - literature review.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Jul 28. doi: 10.1007/s00213-025-06856-1. Online ahead of print. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40719854 Review.
-
Multi-time point transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal key transcription and metabolic features of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.Genes Dis. 2024 Nov 17;12(2):101465. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101465. eCollection 2025 Mar. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 39759115 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Zanthoxyli Pericarpium-Zingiberis Rhizoma in the Treatment of Gastric Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 May 30;19:4537-4566. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S503874. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40464032 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Biomarkers of Fatal Hypothermia Revealed by UHPLC-MS Metabolomics in Mice.Metabolites. 2025 Feb 11;15(2):116. doi: 10.3390/metabo15020116. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 39997741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cannistrà M, Ruggiero M, Zullo A, Gallelli G, Serafini S, Maria M, et al. Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: A systematic review of literature and the role of current drugs and biomarkers. Int. J. Surg. (Lond. Engl.) 2016;33(Suppl 1):S57–70. - PubMed
-
- Peralta C, Jiménez-Castro MB, Gracia-Sancho J. Hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury: effects on the liver sinusoidal milieu. J. Hepatol. 2013;59:1094–1106. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

