Autophagy and autophagy signaling in Epilepsy: possible role of autophagy activator
- PMID: 37880579
- PMCID: PMC10598971
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-023-00742-2
Autophagy and autophagy signaling in Epilepsy: possible role of autophagy activator
Abstract
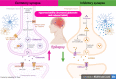
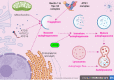
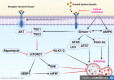
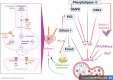
Autophagy is an explicit cellular process to deliver dissimilar cytoplasmic misfolded proteins, lipids and damaged organelles to the lysosomes for degradation and elimination. The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) is the main negative regulator of autophagy. The mTOR pathway is involved in regulating neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, neuronal development and excitability. Exaggerated mTOR activity is associated with the development of temporal lobe epilepsy, genetic and acquired epilepsy, and experimental epilepsy. In particular, mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) is mainly involved in epileptogenesis. The investigation of autophagy's involvement in epilepsy has recently been conducted, focusing on the critical role of rapamycin, an autophagy inducer, in reducing the severity of induced seizures in animal model studies. The induction of autophagy could be an innovative therapeutic strategy in managing epilepsy. Despite the protective role of autophagy against epileptogenesis and epilepsy, its role in status epilepticus (SE) is perplexing and might be beneficial or detrimental. Therefore, the present review aims to revise the possible role of autophagy in epilepsy.
Keywords: Autophagy; Autophagy inducers; Epilepsy; Neurodegeneration; Seizure.
© 2023. The Feinstein Institute for Medical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S. Long-term use of metformin and Alzheimer’s Disease: beneficial or detrimental effects. Inflammopharmacology. 2023:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

